Nowadays, demand for low-power, compact, mobile, and flexible computing machines that interconnect is growing rapidly.
NEED FOR 6LOWPAN
The 6LoWPAN system is used for a variety of applications including wireless sensor networks. This form of wireless sensor network sends data as packets and uses IPv6 – providing the basis for the name – IPv6 over Low-power Wireless Personal Area Networks.
The concept was created because engineers felt the need for the smallest devices which were unable to participate in the Internet of Things and were left out.
6LoWPAN, therefore, allows for the smallest devices with limited processing ability to transmit information wirelessly using an internet protocol IPV6.
It’s a low-power wireless mesh network where every device has its own address that allows the device to connect with the internet using open standards. The targeted applications are those where there is a need for wireless internet connectivity at lower data rates for devices with very limited form factors.
6LoWPAN is low cost, short-range, low memory usage, low bit rate, and comprises edge router and sensor nodes. The edge router is the core of the 6LoWPAN network that links the 6LoWPAN network to the other IP internet. It is responsible for routing the 6LoWPAN packet to the IPv6 packet and assigning IPv6 prefixes in the 6LoWPAN network.
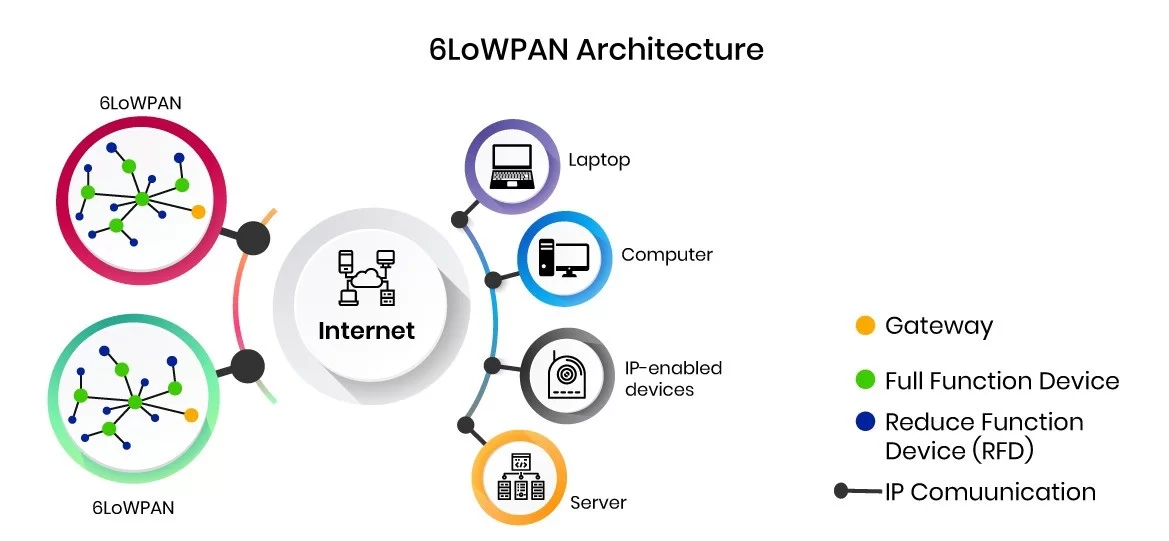
The routing mechanism for 6LoWPAN can be divided as mesh-under and route over, based on the routing decision taken on the adaptation layer or network layer respectively.
A LITTLE ABOUT IPV6 :
IPv6 is the latest version of internet protocol and provides a unique identification and location system for computers on networks across the internet.
IPv6 utilizes 128-bit Internet alphanumeric addresses. Therefore, it can support 2^128 Internet addresses (More than three hundred forty undecillion !!
IPSEC being an inbuilt feature in IPv6 adds to its security. It also supports quality of service (QoS). It allows direct addressing instead of NAT(Used in IPv4) due to the vast address space.
THE MAXIMUM TRANSMISSION PACKET SIZE IN A STANDARD IPV6 IS 1024 BYTES WHEREAS IT IS REDUCED TO 127 BYTES IN 6LOWPAN.
In the IPv6 network, 40 bytes are reserved for the IPv6 header, 25 bytes for the MAC header, additional 8 bytes may also be used for UDP headers. This will make the left-over payload to be about 54 bytes in 6LoWPAN. To offset for the small available frame size of a payload, an adaptation layer has been established by IETF to reduce the IPv6 overhead header.
6LoWPAN is an open standard defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force, IETF. The IETF is the standards body that defines many of the open standards used on the Internet including HTTP, TCP, UDP, and many others.
High IPv6 header compression, Bootstrap, multihoming, and flexibility are some of the important features. since it is IP-based, all these devices can talk to each other with no interference issues.
6LOWPAN INTEROPERABILITY
6LoWPAN can communicate with 802.15.4 devices as well as other types of devices on an IP network link like WiFi.The ZigBee IP is also built on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, but unlike 6LoWPAN protocols, it cannot easily communicate with other protocols.
6LOWPAN IN IOT SECURITY
It is anticipated that the Internet of Things, IoT will offer hackers a huge opportunity to take control of poorly secured devices and also use them to help attack other networks and devices.6LoWPAN uses AES-128 link-layer security which is defined in IEEE 802.15.4 and this provides link authentication and encryption. Further security is provided by the transport layer security mechanisms. This is defined in RFC 5246 and runs over TCP/IP protocol.
BASIC REQUIREMENTS FOR 6LOWPAN :
- The device must have sleep mode in order to support battery saving.
- Minimal memory requirements.
- Routing overhead should be lower.
ADVANTAGES OF 6LOWPAN IN IOT :
One clear advantage of 6LoWPAN is the low power consumption and the meshing capability, enabling the wide dispersion of battery or battery-less sensor nodes into the field. In addition, as this technology is evolving, so does the 6LoWPAN system along with it will evolve more
- Support robust, self-healing, and scalable mesh networking.
- Works efficiently with open IP standardized including UDP, TCP, COAP, HTTP, MQTT, and web sockets.
- In this network, leaf nodes can be in sleep mode for a long duration of time.
- It also offers one-to-many and many-to-one routing.
- It offers end-to-end IP addressable devices which don’t require any gateway, only a router that can connect this network to IP.
- It is a standard: RFC6282.
With the world migrating towards IPv6 packet data, a system such as 6LoWPAN in IoT offers many advantages for low-power wireless sensor networks and other forms of low-power wireless networks.

SELECTION OF A WIRELESS PROTOCOL
When selecting a wireless technology factors must be considered such as power consumption, data rate, range and signal propagation (sub-GHz vs 2.4 GHz), and complying with any FCC or regional air time constraints that may be critical to the application. As a whole, these considerations will ultimately favour one technology or the other.
According to a recent survey, the number of IP-enabled embedded devices is growing at a very rapid rate, and the progress made in the field of low-power radio, microcontroller, and microelectronic technology over the past decade, caused a drift in the industry for smart embedded devices called smart objects to turn out to be IP-enabled, making 6LoWPAN architecture a future-proof solution in the IoT industry.
A brief about what we do at PsiBorg Technologies (IoT Service Provider):
We are specialized in hardware development, wired and wireless connectivity protocols, security, device management, optimized computing at the edge, and complete software for IoT endpoints and gateways.
We are focused on designing and developing a range of smart products and industry solutions with deep customer insights and end-user inputs.
FAQ
Ans. 6LoWPAN is a protocol that allows low-power wireless devices to communicate over IPv6. One important feature is that it supports header compression techniques to minimize the IPv6 packet size. Second, it increases the security and privacy of low-power devices by supporting end-to-end encryption and authentication.
Ans. Yes, 6LoWPAN is designed to be compatible with other IoT communication protocols. For eg- it is used to collect data from a ZigBee sensor. The data can then be transmitted over a 6LoWPAN network to the gateway, which then further forwards the data to the cloud for analysis.
Ans. 6LoWPAN has many existing applications, such as smart homes and building automation, where low-power devices can control and monitor appliances, temperature, and security over IPv6 networks. 6LoWPAN is also used for industrial and environmental monitoring.