WHAT IS EMBEDDED FIRMWARE DEVELOPMENT?
In order to understand what embedded firmware development is, we first need to get an idea of how firmware is different from software. Also as we have software updates in Software applications, likewise we have Fota Update in IoT Applications, and even if we talk about our smartphones. Software and firmware both have data that is read and handled by a processor.
The difference between the two lies in the degree of complexity involved in altering the two.
Software is called “soft” since it is placed in the RAM of the computing system. As soon as the power supply to the system gets cut off, the data that the software needs to work on is lost. Since software data is sourced from the computer system’s permanent memory, it renders itself to change. When the memory data is altered so do the instructions in the program.
On the contrary, Firmware is “firm” because it isn’t easy to alter it once it has been programmed and installed into a hardware device/platform. Just like software, the set of instructions that constitute firmware is stored on a physical device. But these instructions are immutable once the data is placed. Similar to software, the instructions that make up firmware are present on a physical device, but these instructions do not render themselves to any change. This is similar to any computer system’s low-level programming functions. All the Operating system data of computer systems is, in fact, firmware, since it cannot be altered.
WHAT IS FOTA UPDATE IN IOT?
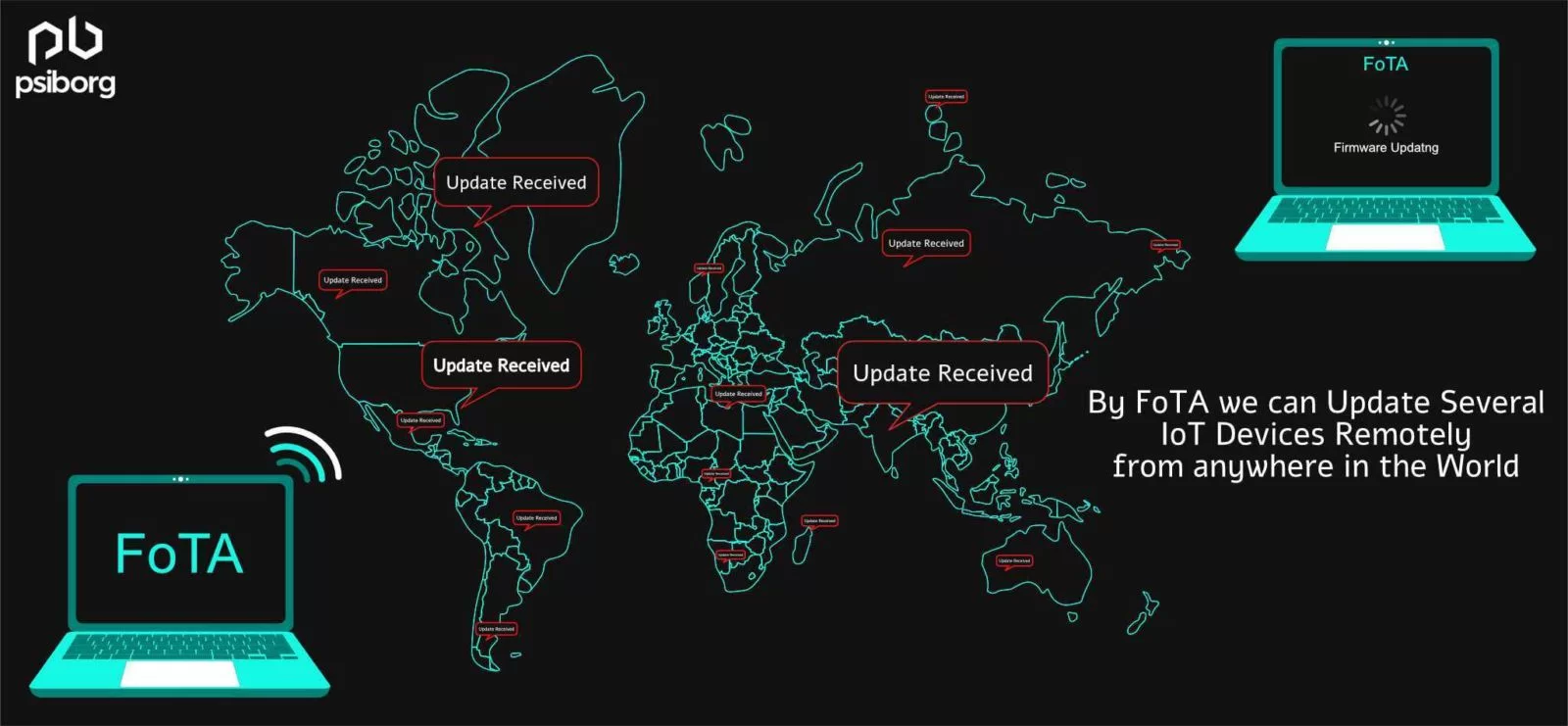
FoTA, which expands as Firmware Over The Air, is the process of changing the hardware code remotely written into an embedded system. This facility is not available on every firmware. It is only present in that firmware that has the appropriate option for remote update of the embedded code.
THE NEED FOR FOTA
FoTA’s need stems from the difficulties faced in updating code in an embedded system by physically accessing it. There are many constraints in physically accessing the embedded system to update its firmware. A connection must be established between the embedded system and a computer to transfer the new program to the embedded system. Such a connection is possible through a USB or a serial adapter.
Another issue with this process is its scalability. The Internet of Things (IoT) is not one device but innumerable devices connected via a network, many of whose locations might not be available. The physical up-gradation of firmware in embedded systems on such a massive scale presents a logistical challenge that necessitates their remote update.
This is why we need the capabilities of FoTA updates in IoT devices.

THE FOTA ADVANTAGES
There are several advantages of having Firmware-over-the-air or FoTA in embedded firmware development. These are listed below:
- Any manufacturer with a sense of responsibility would prefer having FoTA since it gives you the capability of doing damage control in the unfortunate situation of a software bug or malfunction, and security issues in your product.
- The updates with modified functions to the firmware can only be dispatched to subsets of the devices’ with the aim of testing in an application environment. Sensitive handling and open communication with the test customers should be a matter of course.
- Firmware over the air offers many cost advantages over firmware updates that involve physical access to the embedded system. This cost is further reduced by providing a uniform platform for updating large numbers of devices.
- Better sustainability and adaptability of devices with the help of FoTA. As small updates are possible in the FoTA system, software/firmware development teams have the leeway to carry on with their tasks of development even in the post-sales scenario of a product.
WHAT ARE THE BOTTLENECKS IN IMPLEMENTING FOTA IN EMBEDDED FIRMWARE DEVELOPMENT?
- Though FoTA uses the LORAWAN standard network, there are sufficient doubts over how smoothly the system will run on this LORAWAN network.
- There are concerns over the availability of efficient systems that can reliably manage the countless devices that would be there on the IoT network. Equally important is the local software installed on the end devices.
- The challenge increases manifold when one considers IoT devices that are on a mix of different network connections. This is because the communication modes and protocols for FoTA are different for different network types. Devices connected via NBIoT network would require different communication as compared to those connected via LPWAN technology for FoTA. So, a need arises for a degree of homogeneity in communication for FoTA irrespective of the network types being used to connect the IoT devices.
- Smooth processing aside, the other most important and challenging task for successful implementation of FoTA in Embedded firmware development is Security. The FoTA communication channels should be compliant with the strict security standards in place. Also, all updated packages need to be digitally signed. Adequate protection must also be ensured for keys for this both on the side of the manufacturer and in the end IoT device.
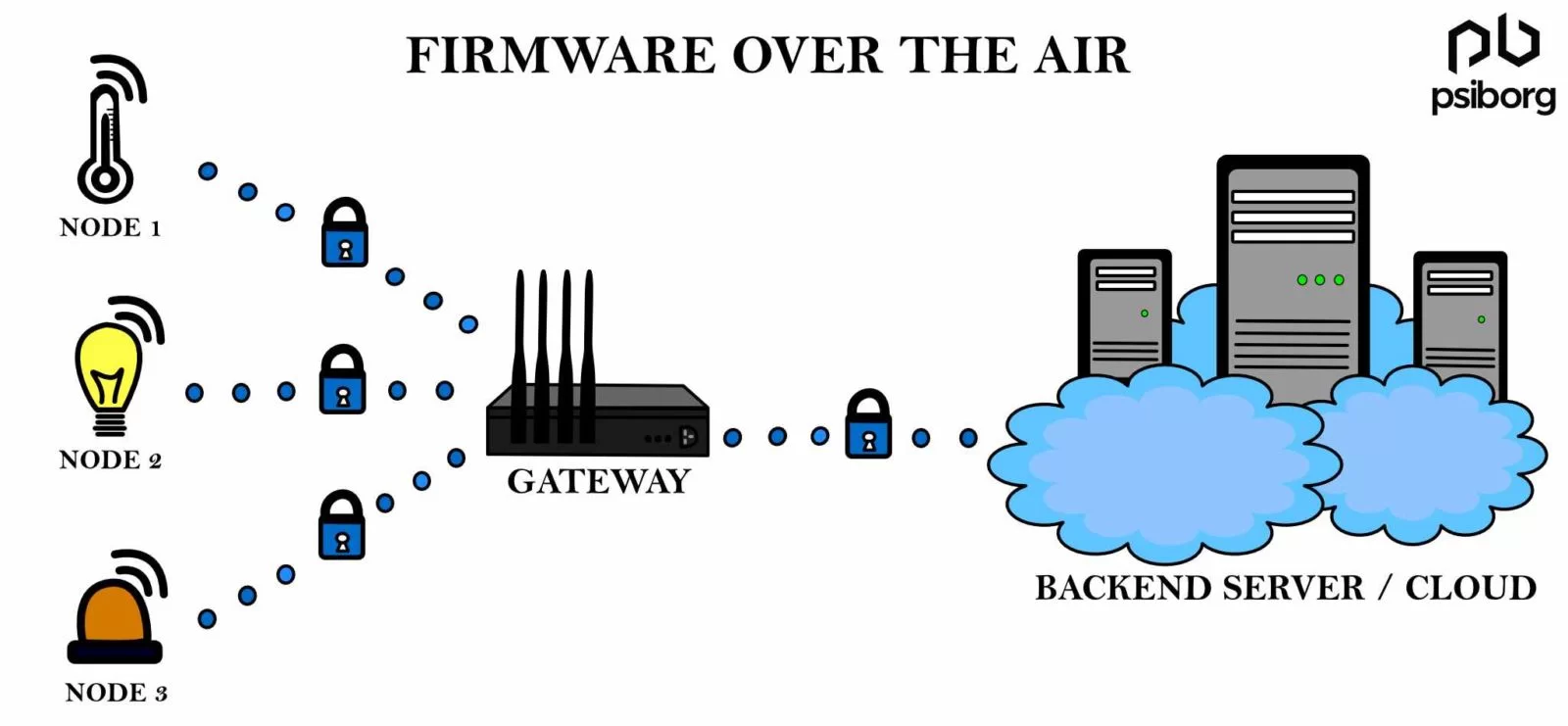
WHAT IS YOUR FOTA STRATEGY?
If you are looking for sensors, adapters and IoT devices that have sufficient flexibility in terms of compatibility for FoTA, they should not be too difficult to find.
Let us assume that you require FOTA capabilities, the question you need to be asking is what is the most cost-effective and reasonable way to implement them? It matters little whether you are aiming for a FoTA solution for a consumer product or a business one. In both cases, you should try for a FoTA solution that is safe, cost-effective and complements your business goals.
PsiBorg offers you the most industry-leading and cutting-edge FoTA solutions to aid your Embedded Firmware Development Strategy in consumer-focused as well as Business IoT products.
We, at PsiBorg, are an IoT solution provider company headquartered in India and serving our clients globally.