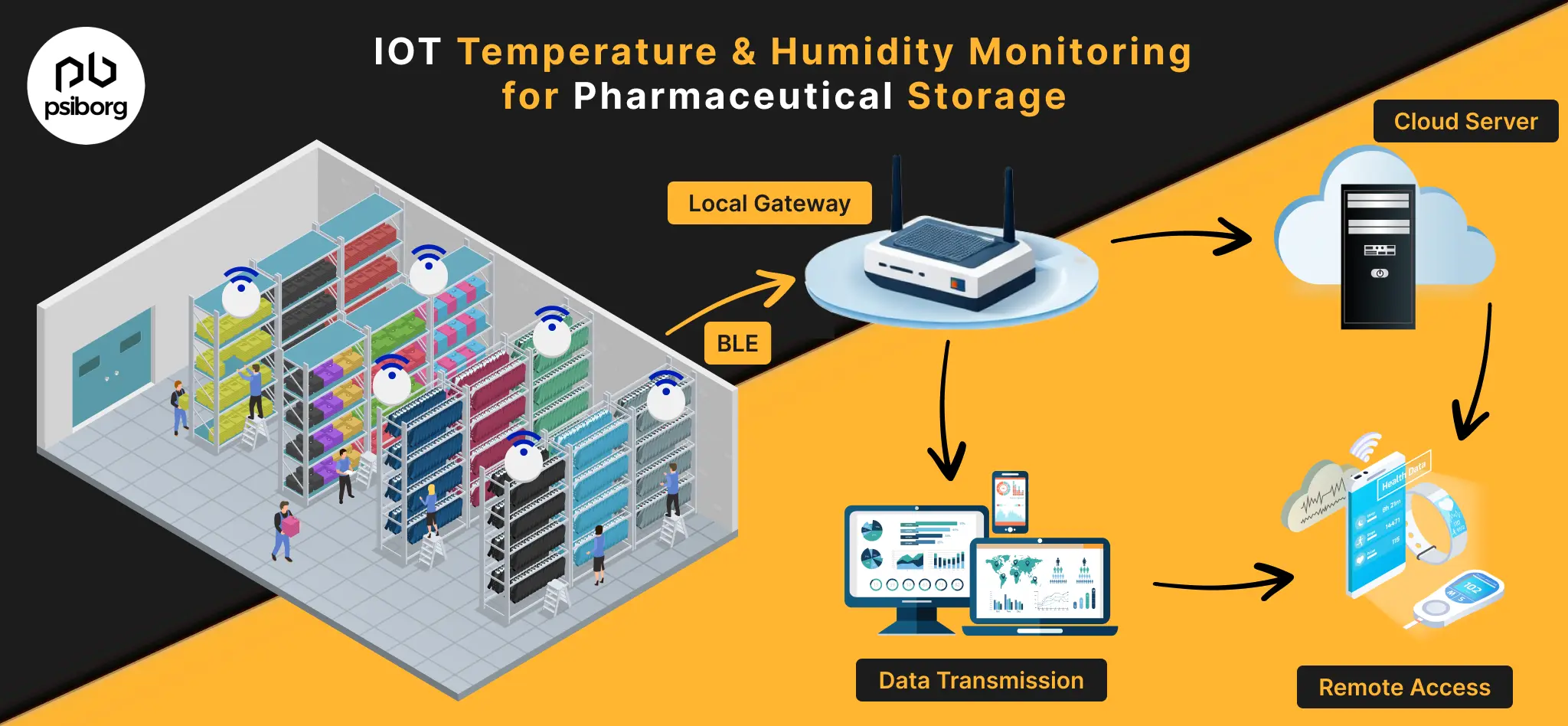
The world of Internet of Things sensors is transforming how different sectors operate. From smartwatches to smart farms, the IoT Sensors are tiny yet powerful devices that make our lives easier, safer and more efficient. They form the core layer of IoT that keeps capturing real-world data and sends it for analysis and required action. But the question is “what are these sensors and what are their real life uses?”. Let’s break that down for you!
What are IoT Sensors?
We’ll begin with the most important part. Basically, IoT sensors are small electronic devices that are designed to sense changes in the real world. They can easily catch the climatic conditions of the place or movements around it and share it with other devices or to the internet. As the name suggests, the Internet of Things literally means that various daily-life objects are connected to the Internet.
In simple terms, they are the senses of smart systems. The sensors collect all the information from the surroundings and share it with smart devices that will either act on it or even notify you when something’s going wrong or unusual.
Why Are IoT Sensors Important?
IoT sensors are known to be highly significant because they help us in:
- Saving energy: They turn off lights or adjust the room temperature automatically according to occupancy.
- Monitoring health: By using smart fitness bands or different medical devices.
- Improving farming: Suggests the right amount of water or fertilizer to be used at the right time.
- Preventing breakdowns: Saves machines by giving us early warnings.
- Keep buildings safe: Sensors that detect smoke or gas leaks help save lives in a building.
These sensors are often found in homes, cars, farms, manufacturing units, hospitals and practically, almost everywhere you can imagine.
Types of IoT Sensors (List of IoT Sensors)
Let’s talk about the different types of sensors in IoT and discuss some of the most commonly used ones in the IoT development industry.
1. Humidity Sensors
The humidity sensor is used to measure the amount of moisture content available in the specimen and is also used to determine the water vapors in the air or gas. The data collected by the humidity sensor are then converted into electrical signals which are further converted into human-readable text. The size and functionality of humidity sensors vary depending on their purpose. Some humidity sensors are embedded into larger systems and used for meteorological purposes, automobiles, medical equipment, HVAC, and manufacturing systems.
Working of a Humidity Sensor
The humidity IoT sensors collect information related to the amount of water vapour present in the air and detect changes in electrical current or temperature in the surroundings. Different humidity sensors work on different working principles to provide the humidity value. The capacitive humidity sensor has a pair of electrodes stuffed with a hydroelectric dielectric which forms a small capacitor. A resistive humidity sensor works by collecting different resistance values. The resistance changes as the humidity changes.

Types of a Humidity Sensor
- Capacitive humidity sensor: Capacitive humidity sensors are used for measuring relative humidity and comprise two different roles for storing electric charge.
- Thermal humidity sensor: Thermal humidity sensors are mostly used for measuring the absolute humidity of a place.
- Resistive humidity sensor: The relative humidity sensor measures the electrical impedance of atoms by utilizing ions.
Applications of Humidity Sensors in IoT
- Soil Quality Monitoring System
- Humidity indicator device
- Refrigerator
- Weather forecast
- Temperature monitoring
- Air pollution measuring system
2. Optical Sensors
Optical sensors are designed to convert light rays into electronic signals and measure the physical value of light. Based on the kind of sensor, the data is translated into a readable format that is integrated into a measuring device. These sensors are particularly suited for contactless counting, protection for positioning of physical parts, etc. Optical sensors are also used to measure velocity, liquid level, temperature, chemical species, displacement, force radiation, electric and electrostatic field, strain, PH value, etc.
Working of an Optical Sensor
The principle on which an optical sensor works is transmitting and receiving light rays. The sensor converts light beams into electronic signals. In basic terms, the optical sensor is used to measure the light quantity physically. The results are then transmitted in a human-readable format. The measurements of the light beam differ based on the object type by which the light beam is reflected. The sensor can be used in various ways, which further categorizes the sensors into 3 types.
- Through-Beam Sensors
- Retro-Reflective Sensors
- Diffuse Reflection Sensors
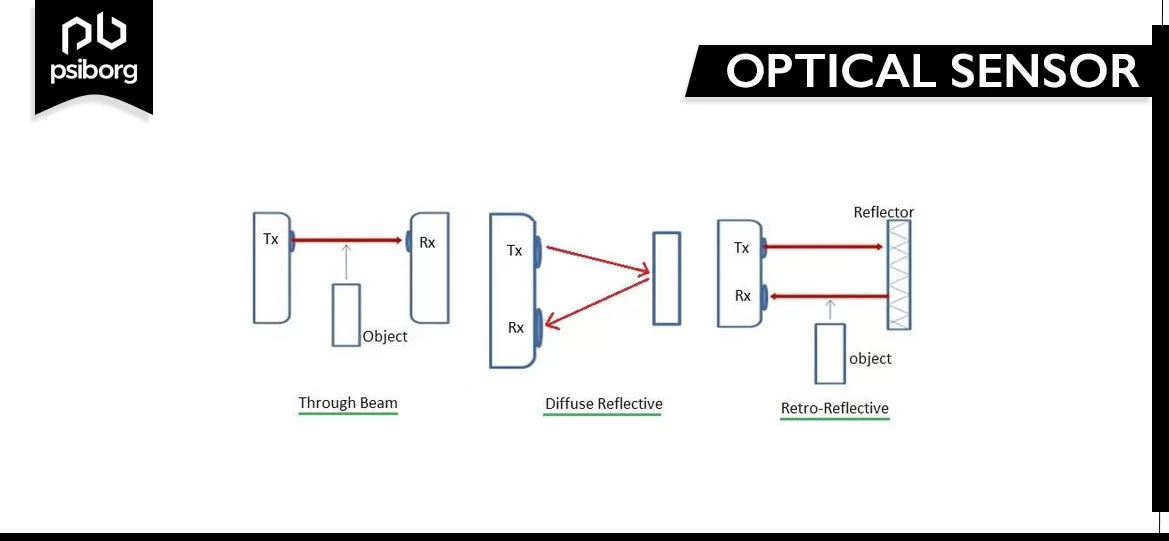
Types of Optical Sensors
- Photoconductive Devices: Covert the change of incident light into the change of resistance.
- Photovoltaic Cell: Converts incident light rays into voltage.
- Photodiodes: Converts incident light rays into currents.
- Phototransistor: Converts incident light rays into current with internal gain.
Applications of Optical Sensors in IoT
- Ambient Light sensors in our phones
- Liquid Level Indicator
- Military and law enforcement
- Camera
- Biometric devices
- Biomedical equipment
- Photo sensing
3. Proximity Sensors
The proximity sensor is a type of non-contact sensor that is used for recognizing the presence of an object when it enters the sensor field. Based on the kind of proximity sensor light, sound, electromagnetic field, and infrared radiation is used for the detection of the target. Usually, proximity sensors are used in recycling plants, anti-aircraft systems, self-driving cars, and smartphones.
Working of a Proximity Sensor
The proximity sensor is used to detect any object. The capacitive proximity sensor can detect any kind of object whereas the inductive proximity can only detect metal. A coil is present in the sensor which produces an electrical field that is generated by providing a power supply to the circuit. Whenever any metal comes into proximity, an eddy current is generated which revolves around the object. As the distance between the sensor and the metal object decreases, the eddy current increases and gives the signals.
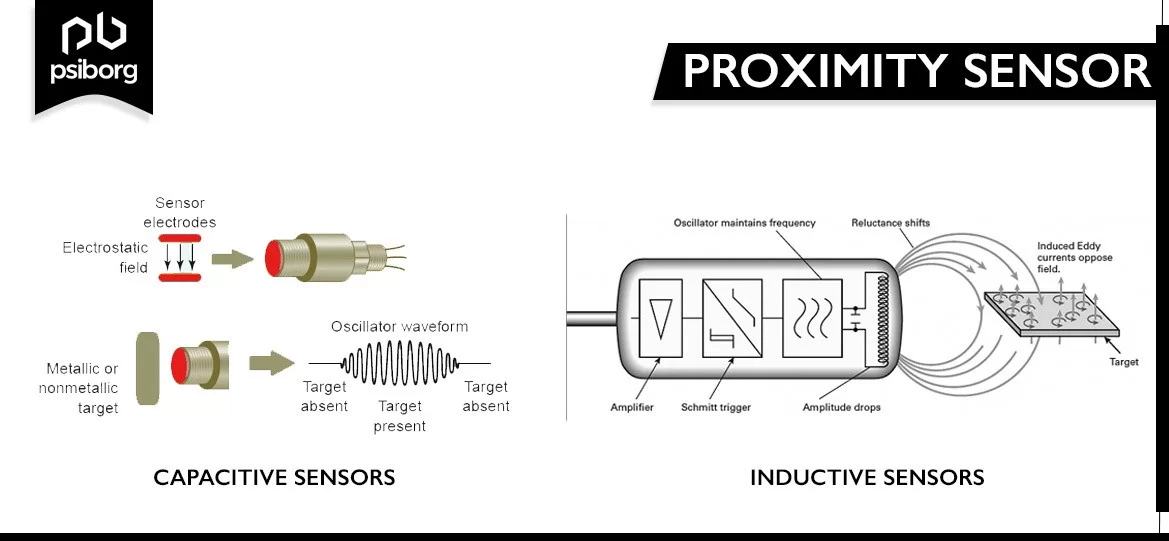
Types of Proximity Sensor
The most common types of proximity sensors are capacitive sensors and inductive sensors.
- Capacitive sensors: These sensors are capable of detecting all kinds of objects that can store electrical charge.
- Inductive sensors: These sensors can only detect metal targets with the help of an electromagnetic field.
Applications of Proximity Sensors in IoT
- Blind stick
- Mobile Phones
- Home automation system
- Automobiles
- Direction sensing device
- Recycling planar craft systems
4. Temperature Sensors
Temperature sensors are devices that can measure the temperature of an object or surroundings and convert them into electronic data. Temperature sensors are used to keep track of temperature changes in an item or place. There are different varieties of temperature sensors, some require physical contact with the item for temperature measurement while others can detect the temperature indirectly.
Working of the Temperature Sensor
The temperature sensor works on the principle of determining temperatures through voltage across the diode terminals. The temperature rise is measured by the increase in voltage. The rise in temperature results in decreased voltage between the transistor terminal emitter and the base present in the diode émitter. The vibrating wire temperature meter is designed on the principle that dissimilar metals have a different linear coefficient of expansion with temperature variation. The wire is specially built and known as a cardio-rite vibrating wire.
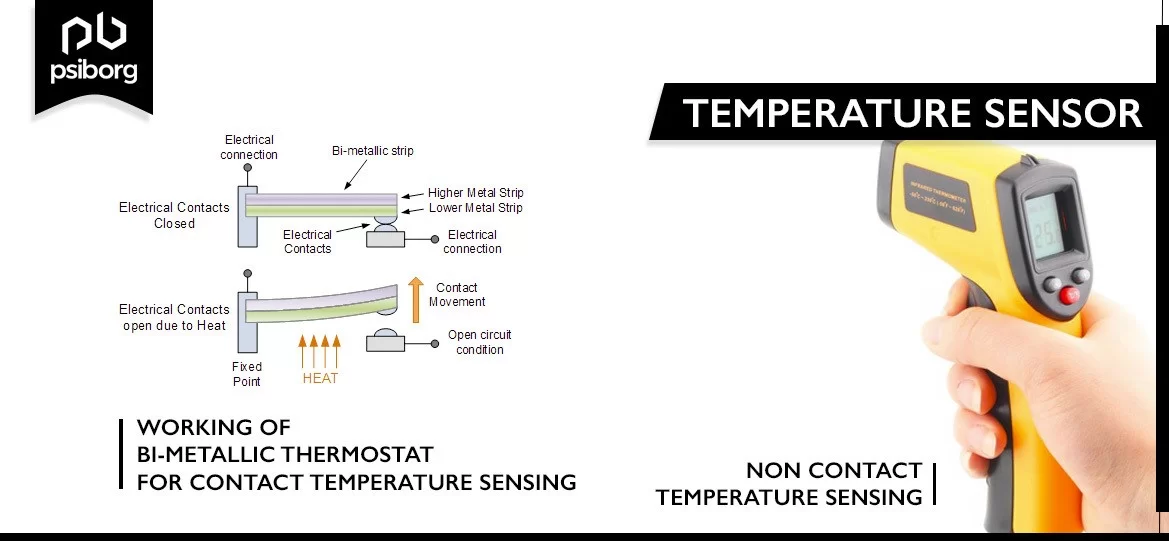
Types of Temperature Sensor
- Contact Type: As the name suggests, the contact type temperature sensor measures the rise or decrease in temperature by directly contacting the object.
- Non Contact type: The temperature rise or fall is measured and the emitted heat radiation from the is required Source. No direct contact is needed to measure the temperature.
Applications of Temperature Sensors in IoT
Temperature sensors are being used in cooking appliances, apparatus, mobiles, and various other types of instruments. Some applications of temperature sensors are:
- Temperature Guns at entry
- Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC)
- Home appliances
- Computers
- Electrical radiators warmers
- Motorsport vehicles
5. IR Sensors
An infrared sensor or IR sensor, as it is popularly known, is a type of electronic component used for detecting and measuring infrared radiation in the environment. Typically infrared radiation is not seen by the human eye because of its longer wavelength compared to visible light. Any object emitting heat at temperatures above 5 Kelvin is an emitter of infrared radiation.
Working of an IR Sensor
The working of an IR sensor is based on two integrated components, i.e. IR transmitter and IR receiver. The IR transmitter transmits infrared radiation which is not visible to humans. These radiations are then detected by the IR receiver. The IR transmitter comes in the form of LEDs whereas the IR receiver is in the form of a photodiode. In simple terms, the IR LED transmits rays that reflect after coming in contact with an object. The reflective rays are received by a photodiode and complete the working of the IR sensor.
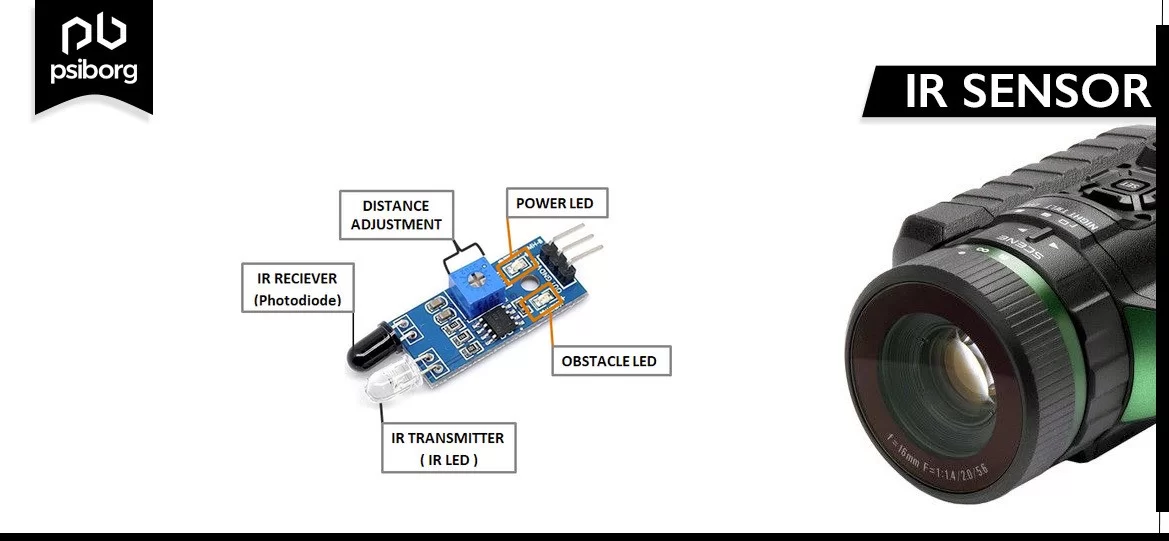
Types of IR Sesnors
Infrared sensors are of two types:
- Active IR sensors: Active sensors can detect as well as emit infrared radiation. Active infrared sensors are used as proximity sensors in obstacle detection.
- Passive IR sensor: On the other hand, passive infrared sensors can only identify infrared radiation from a source. Motion-based detection systems typically use passive infrared sensors.
Applications of IR Sensors in IoT
- Night vision camera
- IR imaging systems
- Infrared tracking
- Radiation thermometer
- Gas detectors
- Flame monitors
6. Electrochemical Sensors
Electrochemical sensors are used for the detection of toxic gases and oxygen in the surroundings; it is used for measuring the concentration of harmful gases in a particular place. Detection of gases is done through oxidation and reduction reactions that generate positive or negative current flow in external circuits.
Working of an Electrochemical Sensor
Electrochemical sensors comprise electrodes, namely the working electrode, a counter electrode, and the reference electrode placed inside a sensor housing immersed in an electrolyte. These sensors work by diffusion of gases that result in the flow of electrons from the working electrode to the counter electrode via the external circuit. The reduction reaction causes an alternative flow of electrons; the concentration of current generated is directly proportional to the volume of gas.
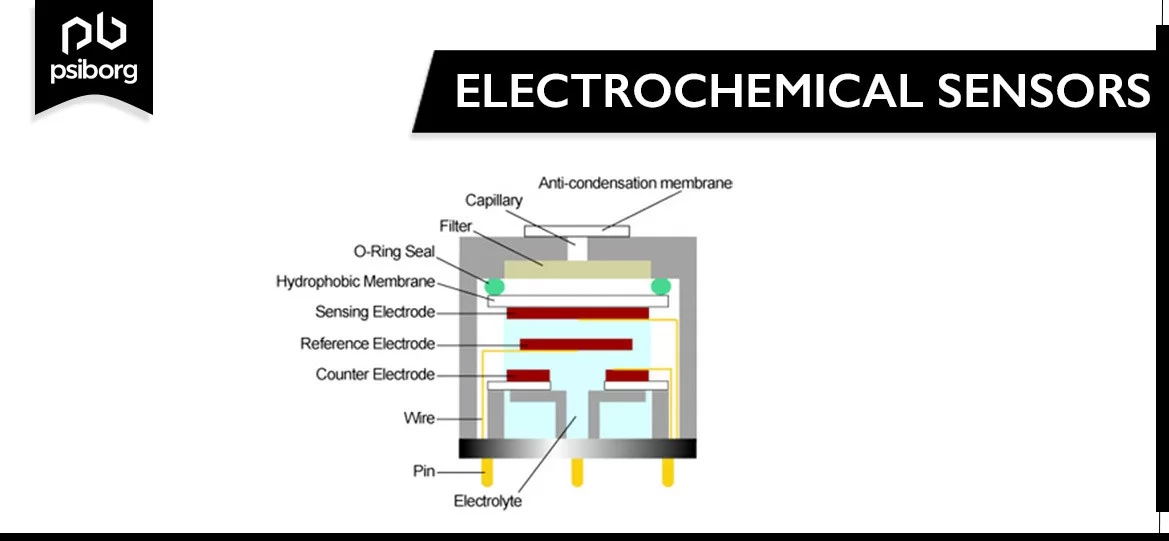
Types of Electrochemical Sensors
- Potentiometric Sensor: In potentiometric sensors, a nearby equilibrium is established in the sensor port, at which both the electrode or membrane potential is quantified, and data regarding the composition of a sample is obtained in the possible gap between two electrodes.
- Amperometric Sensor: The Amperometric Sensor exploits the usage of a potential applied between a benchmark and a working electrode, to induce the oxidation or loss of an electroactive species; the consequent current is measured.
- Conductometric sensors: The conductometric sensors are included with the measurement of conductivity in a set of frequencies.
Applications of Electrochemical Sensors in IoT
- Forensic Drug Analysis
- Medical Diagnostics
- Food Quality Monitoring
- Water Quality Analysis
- Environmental Monitoring System
7. Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors are widely used in the IoT industry for measuring the distance of an object with the help of ultrasonic sound waves. The ultrasonic sound waves get reflected by the object which is then converted into electrical signals.
Working of an Ultrasonic Sensor
The working of ultrasonic sensors can be understood this way. Ultrasonic sensor has two main components i.e. transmitter and receiver. The transmitter transmits ultrasonic sound waves which strike the object and get reflected. The reflected rays are caught by the receiver on the other hand and converted into electrical signals. The sound waves sent by the ultrasonic sensors are not audible to human ears. The distance of the object is calculated with respect to the time taken by the sound waves to reflect back and received by the receiver.

Types of Ultrasonic Sensors
- Defusing Proximity Sensor: Ultrasonic sensors are used to measure the proximity of the object. The proximity type of ultrasonic sensor has a sonic transducer. The transducer sends numerous ultrasonic signals and measures the distance by hearing the sound of waves when returning after reflection.
- Retro-reflective sensor: The object is kept at a specified distance. The name retro reflective is given because the sensor sends a series of sound waves that are reflected by fixed position reflectors.
- Beam sensor: The Beam ultrasonic sensor has two different holders for the transmitter and receiver. The continuous sound waves are transmitted by the transmitter holder and received continuously by the receiver and the holder. Whenever an object comes in between the transmitter and receiver, the sonic beam disrupts. Disruption is taken, as input for distance measurement or to find the intruder.
Applications of Ultrasonic Sensors in IoT
- Self-Parking Automobiles
- Obstacle detectors
- Robotics
- Medical equipment
- Anti-collision detection
- Intrusion Detection
8. Micro-Electromechanical System
The microelectromechanical system is a technology associated with the manufacturing of microscale devices like Sensors, Transducers, Actuators, Gears, Pumps, Switches, etc. If a Sensor is designed and manufactured using MEMS Technology, then it is called a Micromachined Microsensor, or merely a MEMS Sensor Micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) sensors fulfil a variety of purposes in various industries. These are high-precision inertia sensors.
Working of a Micro-Electromechanical System
MEMS is composed of chip technology suspended between capacitive plates. When the sensor is tilted, the change in capacitance is measured as the difference made by suspended mass is detected. This can be measured as an alteration within capacitance. The signal could be changed to produce a stable output signal in digital.
Types of Micro-electromechanical Systems
- Accelerometer: Used for electronic stability
- Magnetometer: Use for direction control
- Pressure sensor: Used to monitor pressure.
- Airflow sensor: used to measure airflow
Applications of Micro-Electromechanical Systems (MEMS in IoT)
- Automotive
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical
- Industrial Automation and Manufacturing
- Defense, Space, and Aeronautical
- Environmental and Health Sciences
- Wearables
9. Acoustic Wave Sensors
An acoustic wave sensor as the name suggests is a sensor that detects acoustic waves. According to the changes in waves, the change in velocity and amplitude can be detected.
Working of an Acoustic Sensor
Acoustic sensors are designed for the detection of acoustic waves that can travel through a material or surface. Changes in the characteristics of the wave are measured and will affect the amplitude and velocity. Velocity changes are recorded by measuring phase characteristics and frequency of the sensor related to the physical quantity. Acoustic waves have differences in their velocities and direction, due to the medium of propagation and boundary conditions sensitivity of acoustic sensors varies due to several factors.
Types of Acoustic Sensors
- Bulk wave sensor: Bulk acoustic wave sensors divide the surface energy through the bulk material to the other surface.
- Surface wave sensor: The surface acoustic sensor focuses the surface energy on the surface itself to make it more sensitive.
Applications of Acoustic Sensors
The telecommunications industry is the largest consumer of acoustic sensors used as bandpass filters. Other applications of acoustic sensors include:
- Medical devices
- Commercial and industrial machinery
- Automobiles
The area of IoT devices is vast and spread to the core of our lives. However, without sensors, it is impossible to think about these devices. Therefore, in conclusion, we can say that sensors are a pillar of the smart technology industry.
The Future of IoT Sensors
IoT sensors are becoming:
- Compact and a lot more affordable
- Smarter with an in-built data processing system
- Capable of running efficiently without batteries using solar energy or movement
- Much more common in everyday life
In today’s world, more and more things are getting connected and automated. Here, IoT sensors are going to be the real heroes behind the scenes.
What We Do at PsiBorg
PsiBorg is an end-to-end IoT solution provider, and hence we love to play with sensors. We have created IoT Sensor networks for various sectors, including smart agriculture, industrial automation etc.
Are you looking for consultation regarding these IoT sensors or do you want someone to assist you in making a new smart solution? If yes, then let’s connect and find the way out to change the world with this fantastic technology called IoT and its building blocks, i.e. sensors.
FAQ
Sensors are central to Internet of Things (IoT) technology. They enable data collection from the physical world, giving data-driven insights for decision-making and automation. Thus, sensors are important for all industrial applications that utilize process control, automation, monitoring, and safety.
Some common challenges that one can face while working with sensors are battery failure and sensor recalibration. Lack of uniform data and connectivity standards can also create challenges during sensor integration. However, protecting sensor data from unauthorized access and ensuring the integrity of sensor measurements is the most challenging part of working with sensors.
IoT sensors are small devices that are smart enough to catch physical changes in the space, like temperature, movement or air quality and convert all the collected information into useful data. This data is used by connected systems or the internet for analysing and acting on it. Together, they make up the foundation of smart devices and systems.
IoT sensors rely on wireless tech like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee or LoRaWAN for data sharing. They send all the collected data to specific gateways, the internet or edge devices. These data receivers properly process, store and finally use the data to take actions or generate useful insights.