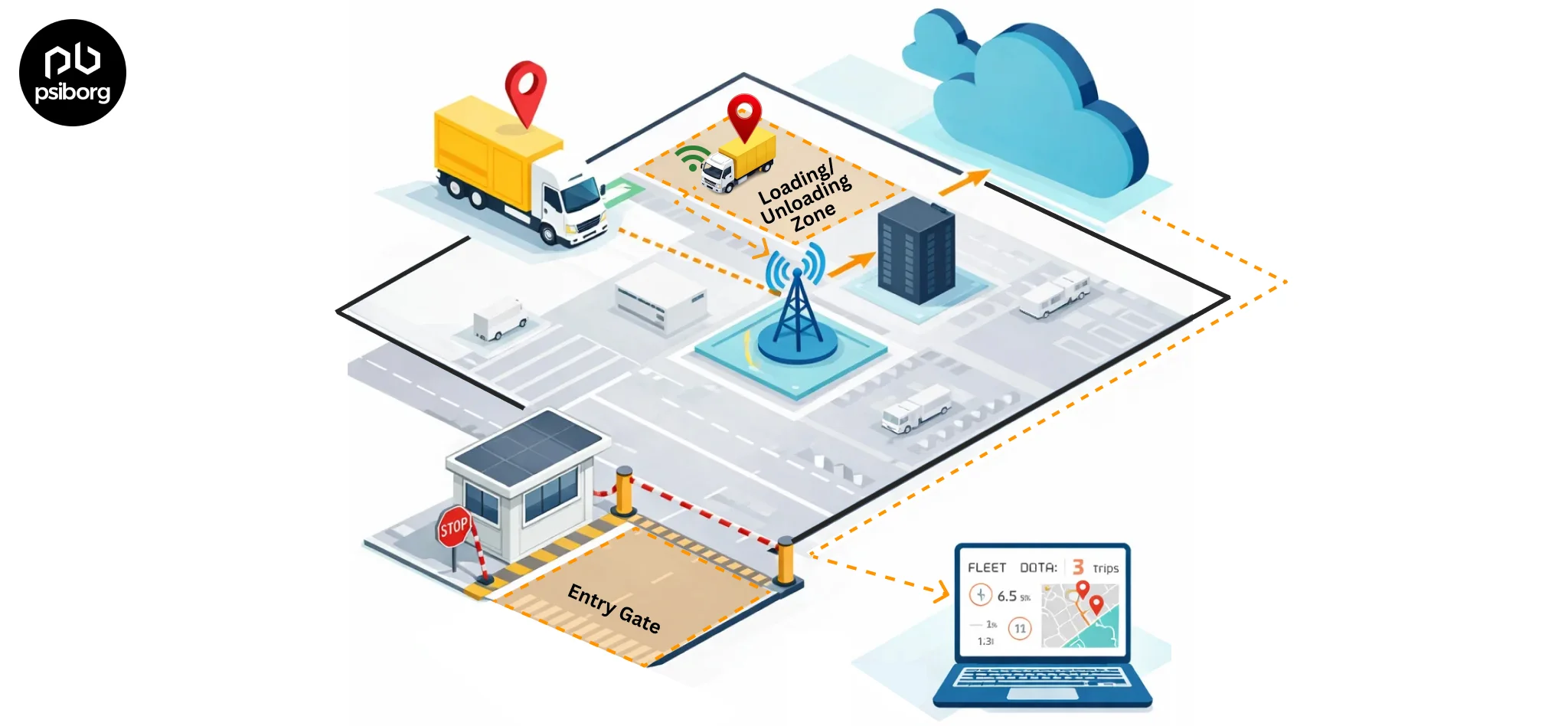
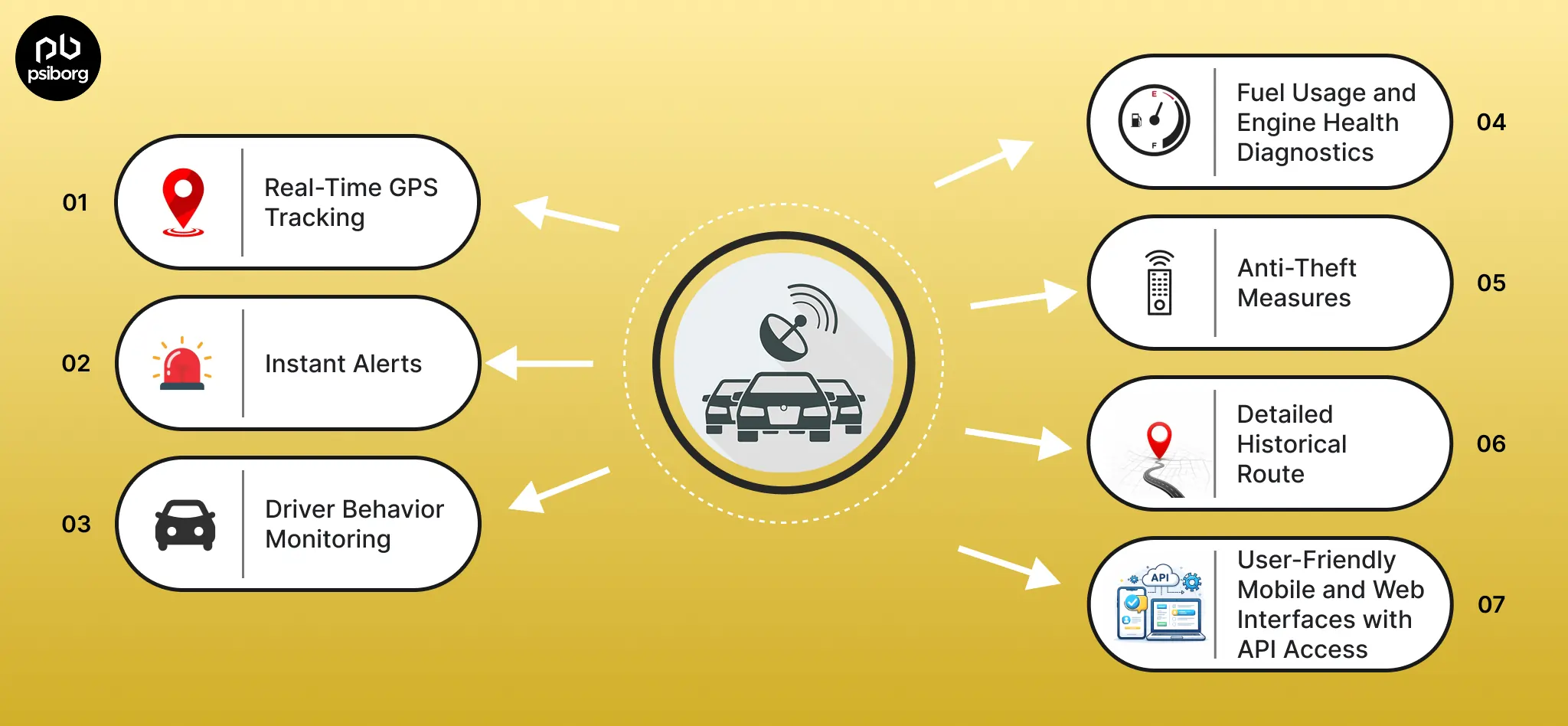
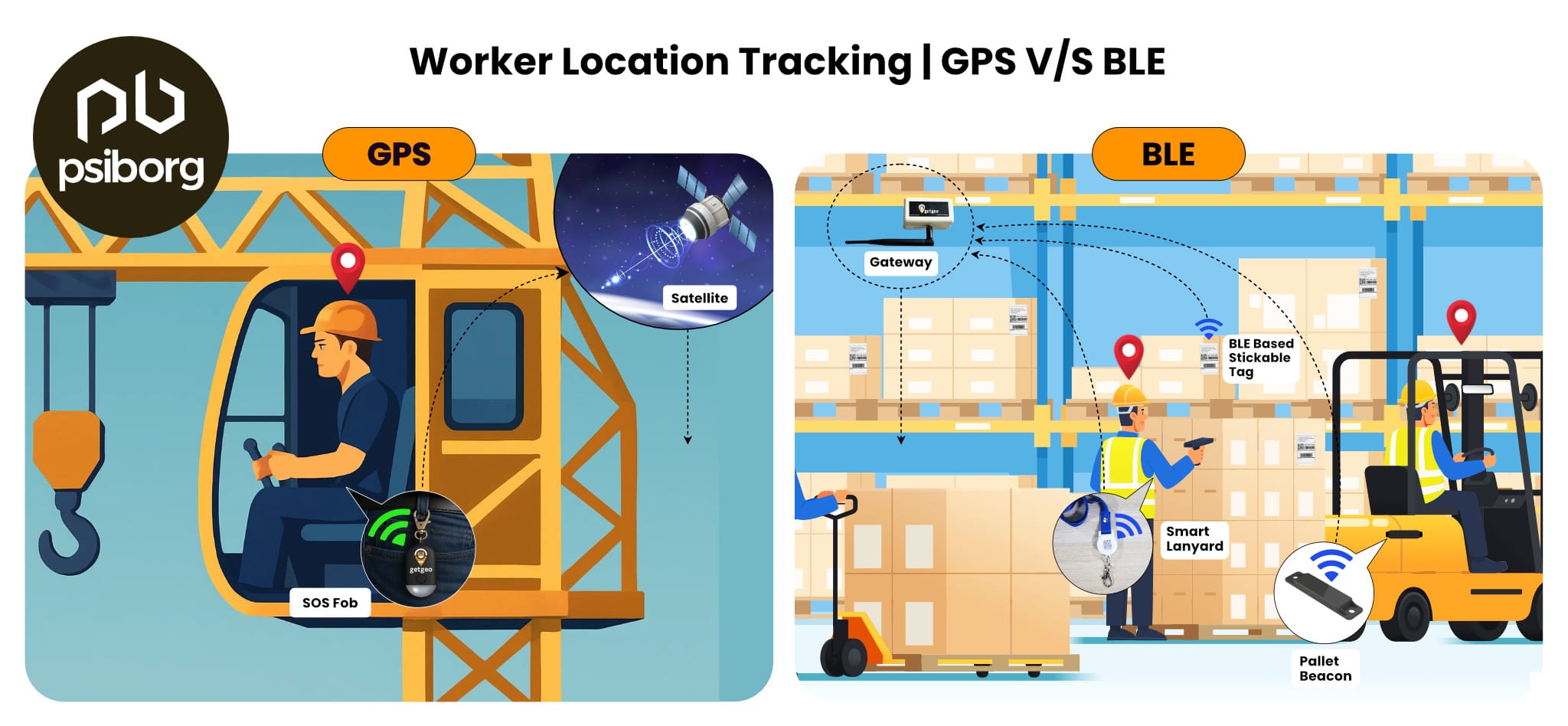
Within a day, a person probably interacts with 100s of connected devices that use multiple wireless protocols and standards. From our smartphones telling us how many steps we walked today to our home security sensors alerting us in case of any anomaly, we have started creating our worlds around IoT. Today, connecting sensors and devices wirelessly through Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, LoRa etc using a 2.4 GHz frequency has become very popular. But unfortunately, this does not have a very long range along with some other disadvantages. Thus, Sensor Network based on Sub 1 GHz came into the picture.
WHAT IS SUB-1 GHZ IN THE FIRST PLACE?
Wireless transmission happens over two kinds of frequencies- high frequency and low frequency. In high-frequency transmission, a very fast speed is achieved. But high-frequency transmission may also lead to the signal being blocked easily by obstacles and distance.
Hence, the need for the usage of low-frequency transmission was felt. The signals could be sent over long distances, had a wider scope and had good signal penetration. In addition to that, it does not even need a high transmission rate or any complex modulation.
Sub-1 GHz literally means a low wireless communication frequency band that is under 1 GHz. Frequency bands that are generally used for IoT communication are 315 MHz, 433 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz, etc. Sensor networks based on Sub-1 GHz have many advantages.
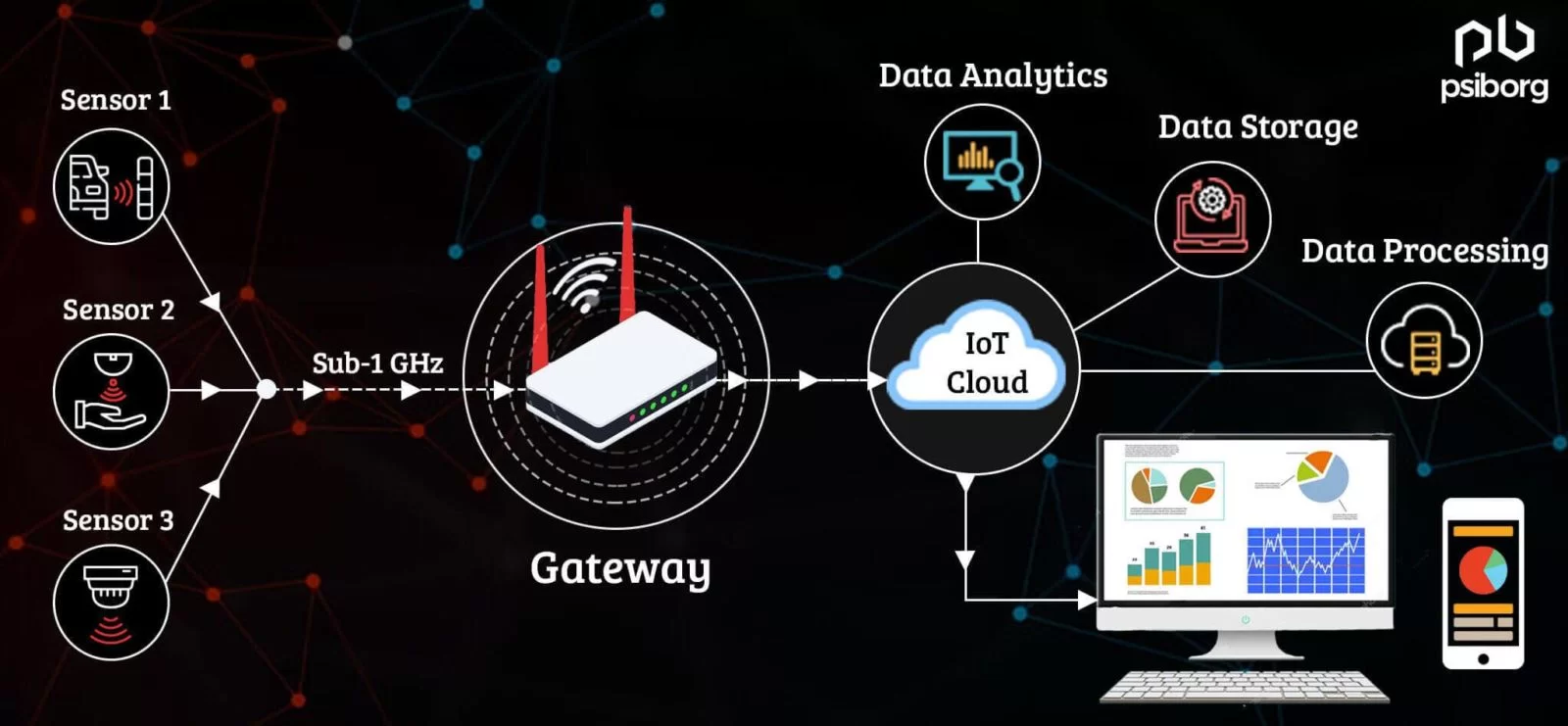
HOW TO CREATE A RELIABLE SENSOR NETWORK BASED ON SUB-1 GHZ?
There are essentially these three factors that need to be taken care of while building a Sensor network based on a Sub-1 GHz LPRF (Low Power Radio Frequency) network-
RELIABILITY
Reliability during communication means minimizing packet loss. So, how can we ensure our packet is not lost? There are several methods like
- Ack/Retry
Ack/Retry means the data is going to be transmitted by the sender until they don’t receive an acknowledgement from the receiver that they have received the message and the correct message. This is possible when the signal strength is relatively short.
- LBT (listen before talk)
LBT is used in radio communication, where the transmitter first senses its environment and then transmits the data. This can be used to find a network where devices are allowed to operate on a free radio channel.
- Short Tx pulses
Short Tx pulses are extremely reliable in the case of battery-operated systems that have many sensor readings.
LOW POWER
Having a low-power system today is extremely important. Just imagine having to charge batteries of thousands of sensors placed in a radius of 10 km or completely changing them every two weeks. This is going to be a very costly affair. Hence, steps are taken so that the power consumption is low. Short Tx pulses and low sleep currents result in low power usage.
OVER-THE-AIR UPDATES
Over the Air (OTA) updates are important because they ensure that the devices will be future-proof. Good downlink data rates and sufficient memory support is used to achieve OTA updates. Updates are sent over a wireless network and distributed among thousands of devices. This method is very convenient and efficient to send any improvement, bug fixes or upgrades.
SOME USE CASES OF SENSOR NETWORK BASED ON SUB-1 GHZ
SMART WASTE MANAGEMENT USING SENSOR NETWORK
In most cities in the world, waste collection and management are difficult and expensive due to operational service costs. Smart waste management plants smart waste containers around the city which detect the level of trash and inform the control centre so that the path of the garbage collection truck can be optimized. This makes sure efficient use of resources along with cleanliness on the streets.
SENSORS BASED AGRICULTURE AND SMART FARMING
Agriculture is the livelihood of most of the people in India. Precision agriculture powered by IoT can help farmers gather information about soil parameters, environmental parameters, number of seeds planted, amount of water and fertilizers required, etc. Farming can become more efficient this way and can lead to more production.
Farmers can also track the health and location of their livestock making use of the IoT technology.
WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK FOR REMOTE MONITORING IN HEALTHCARE
Healthcare Monitoring is probably the most important application of IoT. The applications include remote healthcare monitoring, elderly care, geofencing of patients, providing critical information about chronic diseases, and many more. Today, 2.4 GHz devices that communicate over WiFI and ZigBee are being used because of their low cost and globally licensed free band, but with the growth in the number of sensors, these networks will not be scalable. Hence, we will have to switch to Sub-1 GHz LPRF technology.
In the upcoming years, wireless communication in the Sub-1 GHz band is going to be used extensively. This can result in a more reliable, robust and secure HAN (Home area network). Using the 2.4 GHz frequency band using WiFi and ZigBee is leaving behind a highly congested network. So, Sub-1 GHz frequency bands like the ISM, and 920/950 MHz bands that offer less interfered wireless channels are going to be used.
So, what we take away from here is that the world around us is ever-growing and demands a Sensor network based on Sub-1 GHz for its reliability, low power and long-range.
Also Read: What is Sub 1 GHz Sensor network and how to build one?
We at PsiBorg offer low-power, high-performing, sub-1 GHz Wireless Sensors Network solutions over a wide range of applications.
We can make the devices compatible with the frequency range used in your country for your convenience. Reach us at info@psiborg.in to know more.
PsiBorg is a leading end-to-end IoT Product Development Company, Headquartered in Noida, India, developing IoT products and prototypes for Global Customers.