NB-IoT and LTE-M are the two technologies that are generally considered suitable for communication with devices without external power supply.
In the development of IoT products, communication and connectivity are considered the most important components, making it even more important to choose the best connectivity technology for these products.
LTE-M and NB-IoT are LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Networks) designed for the IoT. However, it can be challenging to choose a particular technology if you don’t know much about it.
That’s why we are writing this blog. Here we will make an unbiased and correct comparison of the two standards based on our IoT experience.
We will try to reduce the complexity and provide an easy-to-understand review of NB-IoT and LTE-M so you can decide whether to choose NB-IoT or LTE-M for your IoT project.
Let’s get started!
WHAT IS LPWAN (LOW-POWER WIDE AREA NETWORK)?
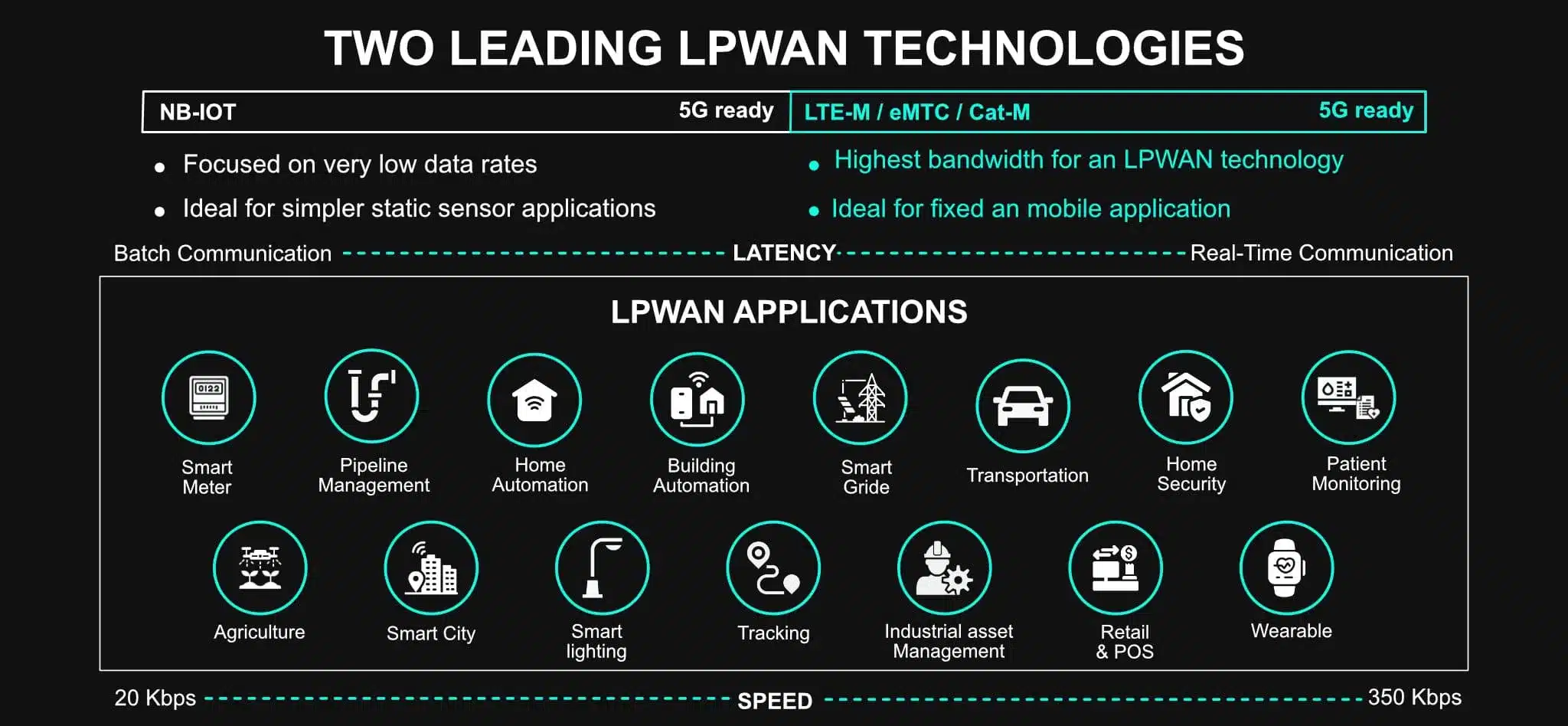
LPWAN (Low-Power Wide Area Network) is a wireless network technology that interconnects low-bandwidth, low-power consumption devices with low bit rates over long ranges, enabling more M2M and IoT applications that were previously prohibitive due to cost.
LPWAN consists of a group of various low-power, wide-area network technologies. You can use licensed or unlicensed frequencies and include proprietary or open standard options.
NB-IoT and LTE-M both belong to the category of LPWAN and are considered the most energy-efficient radio transmission technologies.
Let’s understand in detail the difference between NB-IoT and LTE.
WHAT IS NB-IOT?
NB-IoT stands for Narrowband IoT. It is a wireless technology deployed over cellular networks that is best suited for indoor coverage, low cost, long battery life, and a large number of devices.
NB-IoT limits bandwidth to a single narrow band of 200 kHz, giving peak speeds of 26 kbps. NB-IoT can be deployed “in-band” throughout a standard LTE carrier or “standalone” for deployments in the dedicated spectrum. This means NB-IoT can co-exist with 2G, 3G, and 4G in a device, but devices operating on 2G, 3G, and 4G cannot automatically support NB-IoT.
It also means that NB-IoT is perfect for devices that are located in buildings, remote and hard-to-reach locations. It supports an excellent battery life, exceeding the 10-year mark.
WHAT IS LTE-M?
LTE-M stands for Long Term Evolution of Machines, it is also known as LTE-MTC and LTE Cat M. It is another Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technology that allows the reuse of an LTE installed base with extended coverage.
LTE-MTC stands for LTE- Machine Type Communication (MTC) and was developed by 3GPP to enable devices and services, especially for IoT applications.
LTE-M offers a data rate of 1 Mbps for 3GPP Release 13, rising to 4 Mbps for Release 14, offering greater mobility and voice capability across the network. However, stating the difference between LTE CAT-M1 and LTE CAT-M2 can be a little confusing.
The main difference between them is in terms of data transmission bandwidth.
NARROWBAND-IOT (NB-IOT) AND LTE-M
Narrowband-IoT (NB-IoT) and LTE-M are both 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) standards that operate on the licensed spectrum. While they have similar performance to other standards, they operate on existing cellular infrastructure, allowing service providers to quickly add cellular IoT connectivity to their service portfolios.
The low-power wide-area networks, LTE-M and NB-IoT, are designed and optimized for IoT connectivity and M2M communication.
NB-IoT, also known as CAT-NB1, operates on existing LTE and Global Systems for Mobile (GSM) infrastructure. NB-IoT is developed to enable efficient communication with long battery life for mass-distributed devices.
Telecommunication giants have put together this standard in conjunction with 3GPP because of its benefits like Power Efficiency, Cost Savings, Reliability, Wider Deployment, Deep Penetration & Global Reach.
NBIoT is developed to enable efficient communication and long battery life for mass-distributed devices and uses the already established mobile networks to connect devices.
LTE-M AND NB-IOT: COMPARISON
- Coverage
- Speed
- Power Consumption
- Mobility
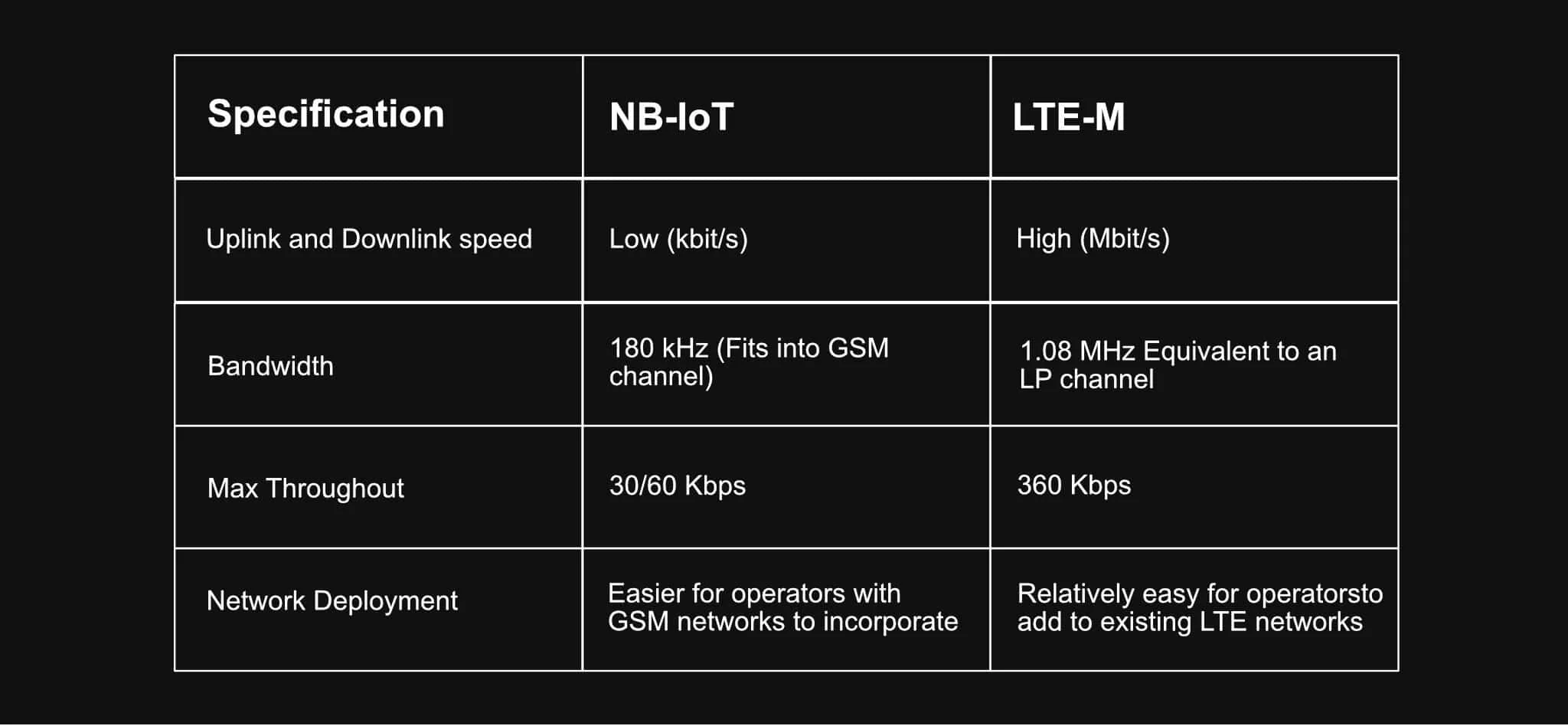
| Specification | NB-IoT | LTE-M |
| Uplink and Downlink Speed | Low (kbit/s) | High (Mbit/s) |
| Bandwidth | 180 kHz (Fits into GSM channel) | 1.08 MHz (Equivalent to an LP channel) |
| Max Throughput | 30/60 Kbps | 360 Kbps |
| Network Deployment | Easier for operators with GSM networks to incorporate | Relatively easy for operators to add to existing LTE networks |
LTE-M VS NB-IOT: COVERAGE
Under tough conditions, LTE-M offers deeper and wider coverage, allowing IoT devices that were previously unreachable to be connected.
NB-IoT connects a huge number of low-cost IoT devices, whether they’re underground, indoors, across the countryside, or in remote places. While NB-IoT has specific advantages for low-bandwidth IoT applications, its roaming is currently limited, and only a few operators have enabled global IoT deployments with multi-network NB-IoT connectivity.
Both NB-IoT and LTE-M are two network standards based on cellular technology, and both are designed to be suitable for enabling worldwide IoT connectivity. Both are future-proof, have worldwide network coverage, and are backed by GSMA and telecom standards.
Since 5G technology is here, new network technologies that allow LPWAN, like LTE-M and NB-IoT (commonly known as Mobile IoT)- are now becoming internationally available.
LTE-M VS NB-IOT: SPEED
LTE-M isn’t extremely fast compared to NB-IoT. Both NB-IoT and LTE-M have limited data transmission capabilities. However, if compared to previous networks and other LPWANs, 1 MB per second for uplink and downlink transmissions is extraordinary. Whether your device needs to download or upload data, the maximum speed will only be a fraction of conventional RAT types.
For most IoT applications, it’s more than enough. LTE-M is best suited for low-data-requirement applications and video-streaming scenarios.
On the other hand, NB-IoT offers a minimum channel bandwidth of 3.75 kHz and can function across a system bandwidth as low as 200 kHz. This leads to unrivaled spectrum flexibility and system capacity.
LTE-M VS NB-IOT: POWER CONSUMPTION
NB-IoT and LTE-M show a noticeable improvement in power consumption as compared to other cellular standards.
Moreover, comparing the above two IoT connectivity solutions is difficult due to many factors that affect power consumption and, thus, battery life. Both LTE-M and NB-IoT technologies support PSM (Power Saving Mode) and eDRX (extended discontinuous reception), which extend battery life.
Moreover, the power consumption of NB-IoT and LTE-M depends on your specific use cases and the devices you use. However, we recommend you thoroughly test all three options- eDRX alone, PSM alone, and eDRX and PSM together. One point to remember is that you cannot misconfigure the sleep period between the wake-respond-sleep cycle so that it doesn’t function as it should.
LTE-M VS NB-IOT: MOBILITY
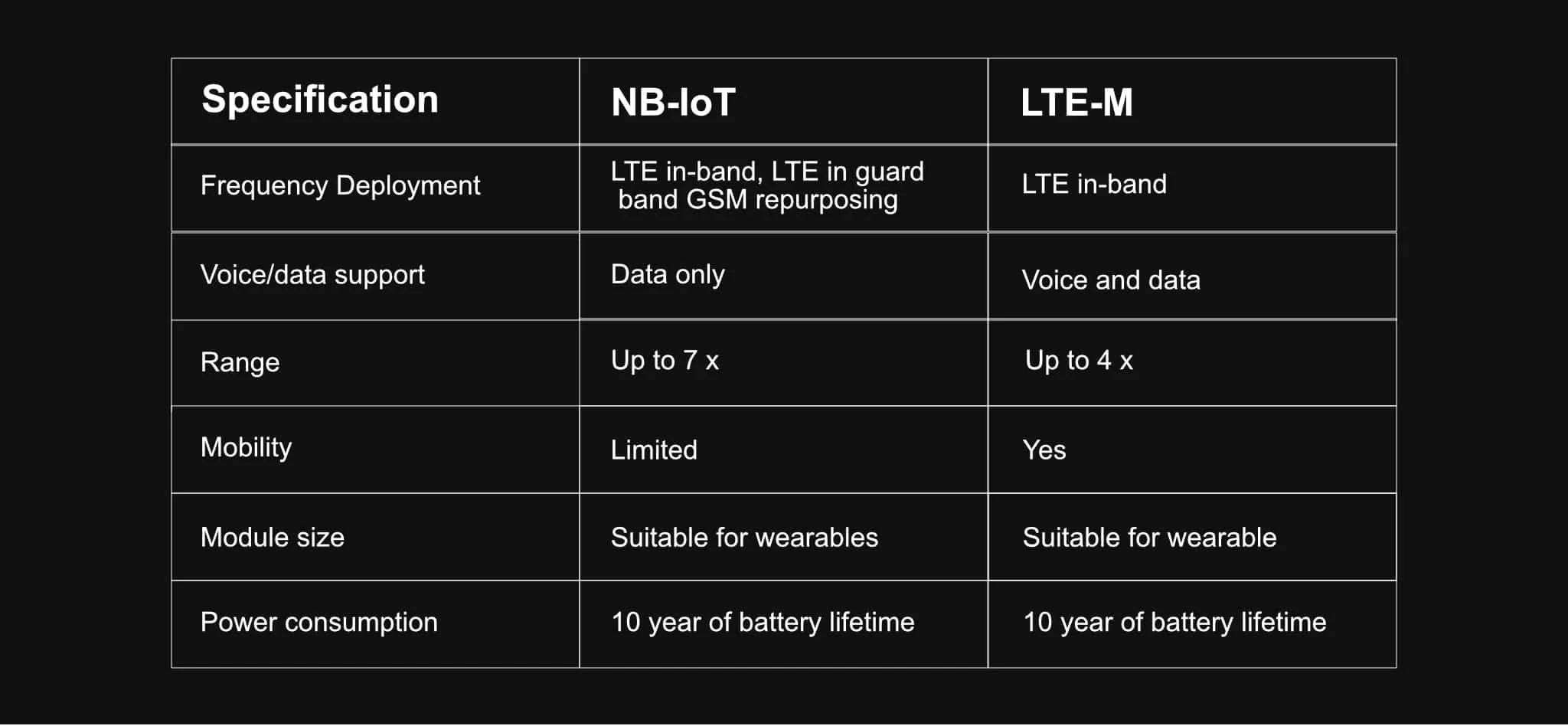
Specification | NB-IoT | LTE-M |
Frequency Deployment | LTE in-band, LTE in guard band, GSM repurposing | LTE in-band |
Voice/Data Support | Data only | Voice and data |
Range | Up to 7x | Up to 4x |
Mobility | Limited | Yes |
Module Size | Suitable for wearables | Suitable for wearable |
Power Consumption | 10 years of battery lifetime | 10 years of battery lifetime |
When your device is in movement, the SIM needs to switch cell towers. NB-IoT can keep the devices connected while they are in movement, but it is not capable of cell tower handover.
When the device moves away from a cell tower, it will maximize the device’s power consumption to try to connect, until it’s completely dark. If disconnected, the device has to re-register with the network, increasing power consumption.
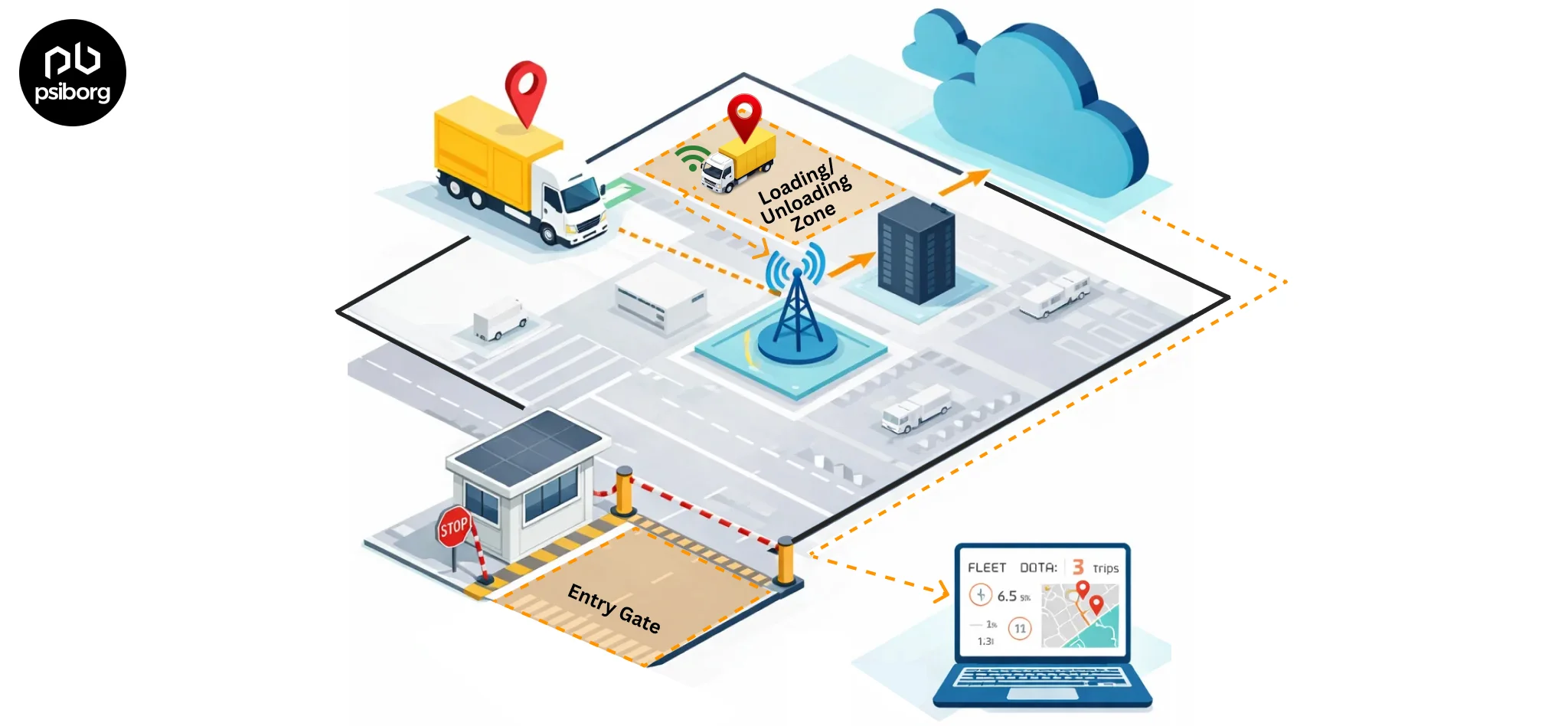
If we talk about LTE-M, it works like 4G and supports seamless switching between different cell towers while saving power. LTE-M supports full mobility and is well-suited for mobile use cases with medium data rate needs like vehicle and asset tracking, fleet management, and more. LTE-M is suitable for both stationary and mobile devices, while NB-IoT is best suited for stationary devices.
NBIOT WORKS IN ONE OF THREE WAYS:
- Independently
- In unused 200-kHz bands that have previously been used for GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications)
- On LTE base stations allocate a resource block to NB-IoT operations or in their guard bands.
Although it has lower bitrates, suitable for applications where data is captured through sensors and sent for computation.
Low cost: The NB-IOT modules have lower costs than the modules & subscription charges for other communication technologies in the market like 3g 4G and LTE-M.
Cellular per cell tower: NB-IOT devices use 180 kHz bandwidth so it is estimated the network can support more than 50000 connections per cell tower.
Uplink and Downlink Speed: up to 62.5kbps
Excellent penetration indoors and underground.
It can be used in Smart metering, Home/Building Automation, Smart Cities & Smart Grid applications.
The advantage of LTE-M, (also known as CAT-M1 or LTE-MTC ) over NB-IoT is its comparatively higher data rate, mobility, and voice over the network, and the highest bandwidth of any LPWAN technology.
It supports a Bandwidth of 1.4MHz
Uplink and Downlink speed: Up to 1 Mbps which is quite more than NB-IoT
VoLTE: Supports voice
Mobility: For devices in movement
The key differences between NBIoT and LTE-M are cost, latency, and speed.
For IoT applications, the revolution – in the form of LTE-M and NB-IoT – is already here. It’s future-proof and will be supported for many years to come with 5G and is thus clearly on the path to 5G.
SUMMING UP,
In a nutshell, both NB-IoT and LTE-M are critical for connecting IoT devices.
However, based on the above comparison, you can see that NB-IoT and LTE-M, both are strong technology standards for IoT applications. In terms of coverage, LTE-M is as good as NB-IoT. Roaming is better with LTE-M and it’s also best suited for static and mobile devices. While NB-IoT is only suitable for static, it also doesn’t offer the freedom to leave.
Although no one can predict the future, it’s impossible to say which LPWAN technology will be more successful. We think LTE-M is the best choice for present-day full-fledged commercial applications.
We hope this blog has helped you learn more about the differences between these two. If you have any further queries, do not hesitate to contact us.
Also Read: LTE-M OR NBIOT: WHICH IS BETTER?
PsiBorg Technologies is considered the best IoT solution provider company, and we have created IoT solutions with both NBIoT and LTE-M, possessing a high amount of expertise in the field.