WHAT IS LPWAN?
A low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) is a type of wireless telecommunication wide area network designed to allow long-range communications at a low bit rate among things(connected objects), such as sensors operated on a battery. A wireless wide area network used primarily for low-power devices is known as a Low-Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN). The sensor devices communicate on LPWAN in the Wireless sensor network.
COMMONLY USED LPWAN TECHNOLOGIES:
- SUB-1 GHZ
- NBIOT
- ZIGBEE
- LORAWAN
- LTE CAT-M1 OR LTE-M
- SIGFOX
WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK (WSN) USING LPWAN TECHNOLOGY
A Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) is a network of distributed and autonomous devices that use sensors to track what’s happening around. The sensor nodes used in WSN systems are integrated with the onboard controllers. The complete circuitry manages the operation and monitors it mainly. Everything is connected with the base station known as the Gateway, where the high-end processing of data collected from distributed sensors is done.
All the distributed sensor devices in WSN are mostly connected over an LPWAN technology and communicate with the gateway.
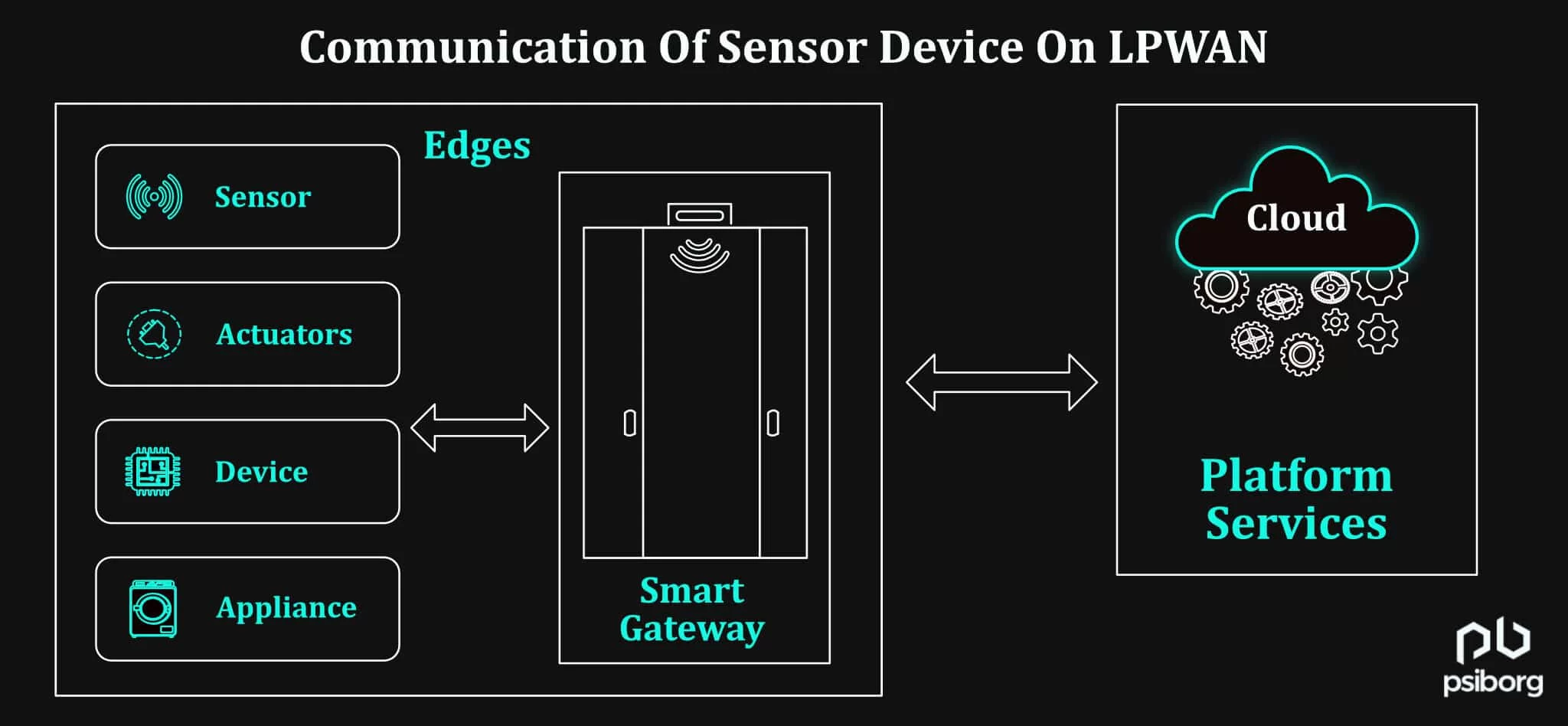
HOW DO SENSOR DEVICES COMMUNICATE ON LPWAN?
A wireless sensor node is equipped with sensing and computing devices, radio transceivers, and power components. The individual nodes in a wireless sensor network (WSN) are inherently resource-constrained: they have limited processing speed, storage capacity, and communication bandwidth. The sensor nodes communicate among themselves using radio signals.
After the sensor nodes are deployed, they are responsible for self-organizing an appropriate network infrastructure often with multi-hop communication with them. Then the onboard sensors start collecting information of interest.
Wireless sensor devices also respond to queries sent from a control site or the gateway, to perform specific instructions or provide sensing
WHAT IS A GATEWAY UNIT IN LPWAN? HOW DO SENSOR DEVICES COMMUNICATE WITH A GATEWAY LPWAN?
The Gateway acts as a bridge between the WSN or other networks and the cloud. This enables data to be stored and processed by devices with more resources, in a remotely located server which is known as a gateway unit.
Edge Computing and Cloud computing both has an important role in IoT applications.
Gateway or Edge Gateway is a device that allows the management (control) of the network and aggregates the information received from the nodes to send real-time or near real-time data to a user platform. When the gateway is connected to a local laptop, the user can locally control and monitor the WSN. Adding a cellular modem (works on LTE, NBIoT, LTE-catM1, etc) or an Internet modem (works on wifi) to the gateway guarantees remote management and sends data to the cloud.
The gateway is important because it coordinates the communication aspect of the WSN as well as its sleeping protocol. At a given time, the gateway wakes up nodes, data is exchanged, and then the nodes go back to sleep. Sleeping is necessary for WSNs to save power. A sensor node generally spends 90% of its time sleeping.
IoT Gateways manage device connectivity, data filtering, processing, protocol translation, security, etc. Some of the newer gateways also function as platforms for application code by processing data.
COMMUNICATION OF COLLECTED SENSOR DATA TO THE CLOUD IN LPWAN
IoT Gateway devices sit at the intersection of the cloud and IoT device nodes or sensor devices connecting over LPWAN. The data collected from wireless sensor networks or other IoT devices will be transmitted through gateways to the cloud. The received data is then stored in the cloud and from there it is provided as a service to the users.
Cloud IoT Core is a fully managed service from Google that allows to easily and securely connect, manage, and ingest data from millions of globally dispersed devices.
Cloud IoT Core supports two protocols for device connection and communication: MQTT and HTTP. Devices communicate with Cloud IoT Core across a “bridge” — either the MQTT bridge or the HTTP bridge. The MQTT/HTTP bridge is a central component of the Cloud IoT Core.
When you create a device registry, you select protocols to enable: MQTT, HTTP, or both.
- MQTT is a standard publish/subscribe protocol that is frequently used and supported by embedded devices, and is also common in machine-to-machine interactions.
- HTTP is a “connectionless” protocol: with the HTTP bridge, devices do not maintain a connection to Cloud IoT Core. Instead, they send requests and receive responses. Cloud IoT Core supports HTTP 1.1 only.
VISUALIZING DATA COLLECTED FROM SENSOR DEVICES ON A MOBILE APP OR IOT DASHBOARD
The data generated from IoT devices is analyzed with respect to time. The timestamp data is processed and this data is pushed to the IoT devices’ cloud storage, forming a database. The IoT Dashboard reads the data from the database and creates data visuals for the user.
The IoT Dashboard is said to be useful only if it can load data efficiently and create visuals from the database. Some IoT web apps provide users with an optimized experience by coupling the data (which is collected through remotely distributed smart devices) with its own database.
CONCLUSION
CAT-M, NB-IoT, Sigfox, and LoRa are key technologies for LPWA applications that have enabled several million connected devices already. In competitive market situations, selecting the right technology is a challenge.
While licensed LPWAN is more suitable for the area with the wide deployment of suitable mobile networks, unlicensed LPWAN is preferred for applications involving industrial, warehouse, and agriculture applications.
Lora and Sigfox were the early entrants in the market and gradually gained the upper hand in terms of unit cost and battery life wherein NB-IoT is still evolving and is yet to be widely deployed and tested. However, CAT-M has created a unique place for itself, facing fewer challenges in this segment because of its support for a higher data rate.
Also Read-: Comparison between NBIoT and LTE-M and LPWAN AND SENSOR DEVICES — HOW DO THEY COME TOGETHER?
What we do at PsiBorg
LPWAN technology is a fantastic technology that is changing the way of communication between IoT devices. If you have a project where LPWAN technology is required, then PsiBorg can help you out.
We are a team of experienced developers with profound knowledge of integrating various LPWAN technologies in IoT sensor networks and created the associated Best IoT dashboard with huge creativity and innovation. Connect with us today for more information.