Ever had a delivery truck vanish into a dead zone, burning cash on fuel and overtime while customers fume?
You’re nodding, right? This is a daily challenge for many logistics and industrial operations relying on outdated tracking systems. However, what if you could pinpoint every vehicle in your fleet, even across remote regions, using devices that run for years on a single battery?
That’s exactly the advantage a LoRaWAN GPS tracking device brings to modern fleets. As industries rapidly digitize, vehicle tracking is no longer a luxury, it’s a necessity. In fact, fleet telematics adoption is projected to grow from $25.5 billion in 2021 to $63.7 billion by 2030, driven by IoT-powered optimization and real-time visibility.
In this blog, you’ll discover how LoRaWAN GPS tracking works, why it’s transforming vehicle monitoring across industries, and how businesses are using long-range, low-power solutions to save time, cut operational costs, and gain complete control over fleet performance.
What is a LoRaWAN GPS Tracking Device?
A LoRaWAN GPS tracking device is a low-power, long-range IoT tracker designed to capture precise location data and transmit it over LoRaWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) instead of traditional cellular networks.
Unlike conventional GPS trackers that rely on power-hungry SIM cards and expensive data plans, LoRaWAN GPS devices are built for:
- Ultra-low power consumption (lasting years on a single battery)
- Long-distance communication (up to 5–10 km in rural areas)
- Reliable tracking even where cellular coverage is weak
To truly understand why LoRaWAN GPS tracking devices deliver long-range performance with minimal power usage, it’s important to look inside the technology that makes it all possible.
Core Components That Power a LoRaWAN GPS Tracking Device
A LoRaWAN GPS tracker is more than just a GPS chip and a radio, it’s an integrated hardware system built to deliver reliable, long-range tracking with extreme energy efficiency.
Let’s break down the specific parts, why they matter, and how they work together:
1. Multi-GNSS Module (Accurate Location in Any Environment)
A LoRaWAN GPS tracking device uses a multi-GNSS engine that connects to GPS, GLONASS, and BeiDou satellites simultaneously to deliver precise vehicle positioning.
By selecting the strongest available signals in real time, the device achieves:
- Faster location fixes after sleep cycles
- Reliable tracking in dense cities and remote areas
- Consistent accuracy with fewer signal dropouts
This multi-satellite approach ensures continuous fleet visibility, enabling better routing decisions, reduced delays, and stronger operational control across wide industrial environments.
2. LoRaWAN Communication Module (Long-Range, Low-Cost Data Transfer)
The LoRaWAN radio module transmits GPS and sensor data over kilometers of coverage using low-power wireless signals instead of cellular networks. Key advantages include:
- Ultra-low energy usage for multi-year battery life
- Wide-area coverage across industrial zones and rural regions
- No recurring SIM or data charges
This allows businesses to track large fleets reliably while keeping connectivity costs predictable and minimal.
3. Low-Power Battery System (Designed for Multi-Year Operation)
LoRaWAN GPS tracking devices are engineered with energy-efficient power management that limits consumption during both positioning and data transmission. This results in:
- 3 to 10+ years of battery life depending on reporting frequency
- Reduced maintenance and replacement costs
- Scalable deployments without frequent downtime
4. Embedded Sensors (Smarter Monitoring Beyond Location)
Built-in sensors add operational context to raw GPS data, enabling automated insights and alerts.Common sensors include:
- Accelerometers for motion and impact detection
- Tamper sensors for unauthorized access alerts
- Temperature sensors for sensitive cargo or harsh environments
Together, these sensors improve safety, prevent losses, and support data-driven fleet management.
Now that you understand what powers a LoRaWAN GPS tracking device internally, let’s follow what happens to that data, from the moment a vehicle moves to the instant you see its location on your dashboard.
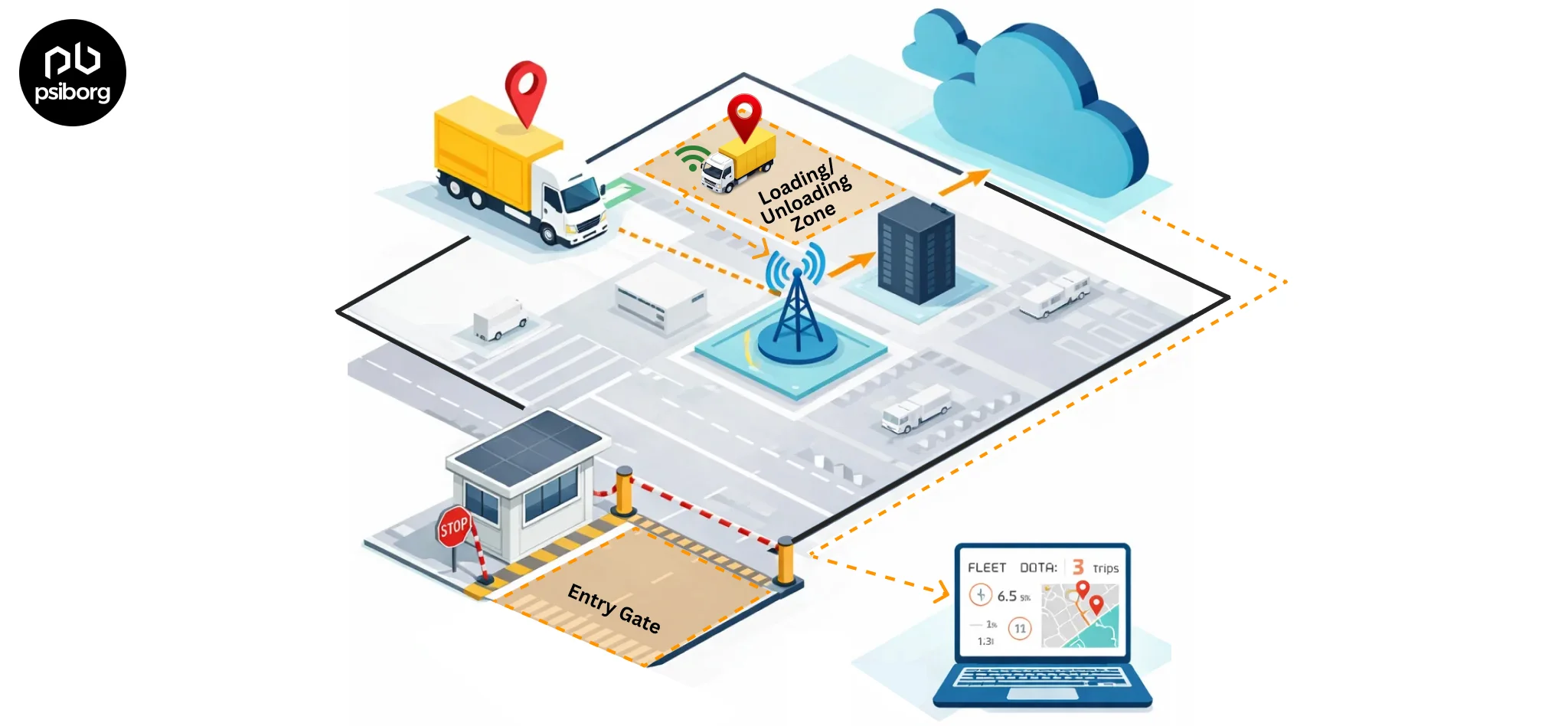
How LoRaWAN GPS Tracking Works?
Once installed on a vehicle, a LoRaWAN GPS tracking device operates in intelligent low-power cycles instead of continuous transmission. The multi-GNSS module activates only when required, such as when the vehicle starts moving, stops, or reaches predefined intervals, and captures highly accurate location coordinates.
To keep energy consumption minimal, the device then compresses this data into lightweight packets and transmits it using its LoRaWAN radio.
Thanks to LoRaWAN’s long-range signal capability and strong penetration through buildings and terrain, the information reaches nearby gateways even in industrial parks, highways, and remote operational zones where cellular networks often fail.
Behind the scenes, the process continues smoothly:
- The gateway receives the signal and forwards it securely to the LoRaWAN network server
- The server authenticates and decrypts the data to ensure reliability and security
- The information is routed to cloud platforms for processing and visualization
From there, fleet managers access:
- Real-time vehicle locations on dashboards
- Automated alerts for geofence breaches, delays, or unusual movement
- Performance analytics on routes, idle time, and utilization.
Because updates are triggered by events or optimized schedules, not constant streaming, this architecture dramatically reduces power consumption while maintaining dependable visibility.
With a clear view of how data moves from vehicles to the cloud, let’s now look under the hood at the complete technology stack that makes LoRaWAN GPS tracking reliable, scalable, and cost-efficient for industrial use.
Must-Have Features in a High-Performance LoRaWAN Truck Tracking Device
Selecting the right LoRaWAN GPS tracking device directly impacts tracking accuracy, operational costs, and system scalability. The best devices combine advanced positioning, efficient power management, rugged design, and smart data capabilities to perform reliably in industrial environments.
Let’s break down the most important features businesses should prioritize.
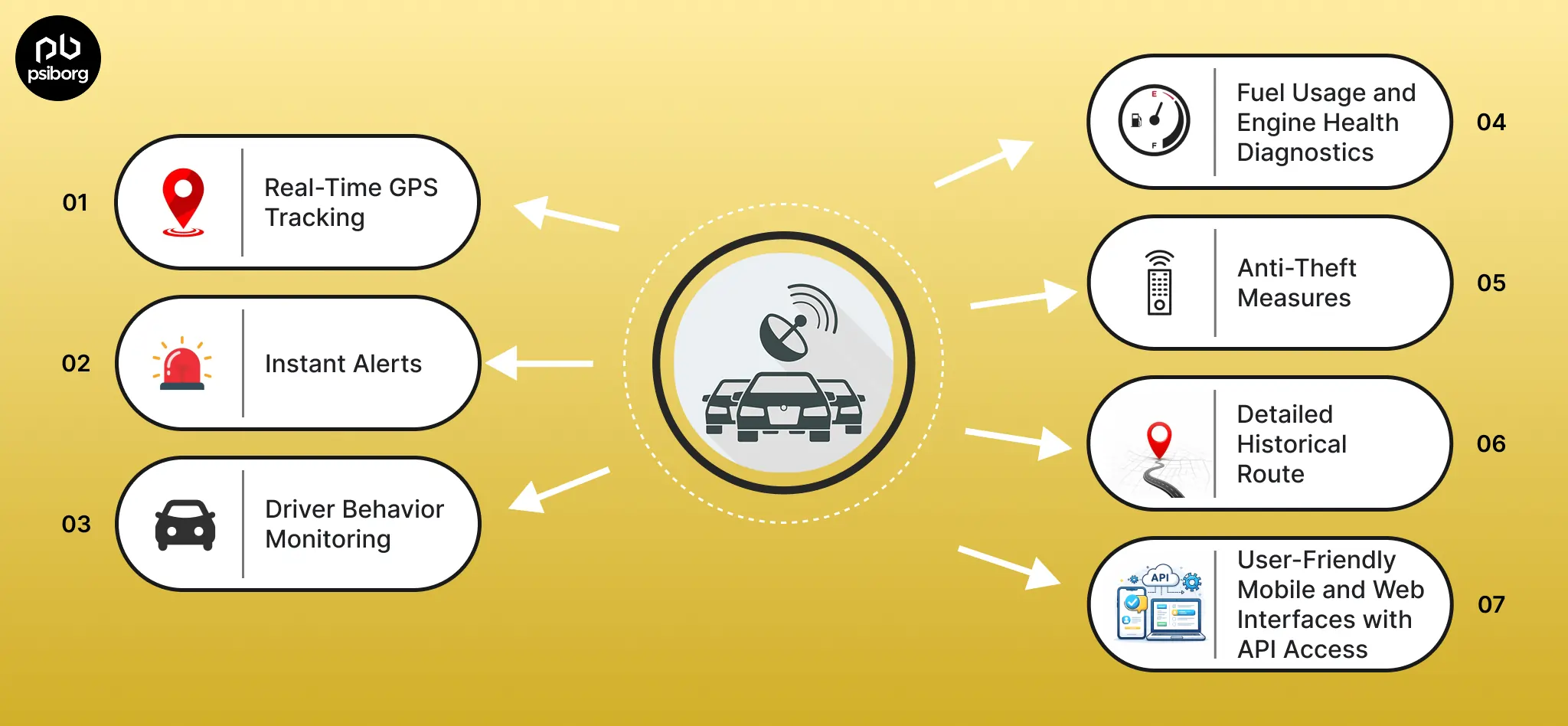
Zone-Based Vehicle Tracking (Geofencing)
This feature allows businesses to define virtual zones such as depots, loading bays, factories, or restricted areas. The device automatically triggers alerts when a vehicle enters or exits these zones, enabling tighter operational control, compliance monitoring, and faster response to deviations.
Vehicle Entry & Exit Monitoring
Entry–exit tracking records precise timestamps whenever a vehicle arrives at or leaves a facility. This helps businesses measure turnaround time, verify delivery schedules, and identify bottlenecks at warehouses, plants, or industrial sites without manual logging.
Vehicle Idle Time Monitoring
Idle time monitoring detects when a vehicle is running but stationary for extended periods. By identifying unnecessary idling, businesses can reduce fuel waste, lower emissions, and improve driver discipline, directly impacting operating costs.
Truck Standing Time Tracking
Standing time tracking measures how long a vehicle remains parked at specific locations such as docks or checkpoints. This insight helps optimize loading processes, reduce delays, and improve fleet utilization across high-traffic industrial environments.
Integrated Sensors for Smarter Insights
Beyond location tracking, devices include accelerometers, tamper detection, and temperature sensors. These sensors provide additional context by identifying movement patterns, unauthorized access, or environmental conditions. This allows businesses to automate alerts, improve security, and monitor sensitive cargo effectively.
Once you’ve selected a device with the right features and technology stack, the real value comes into play, how LoRaWAN GPS tracking transforms everyday operations and delivers measurable business results.
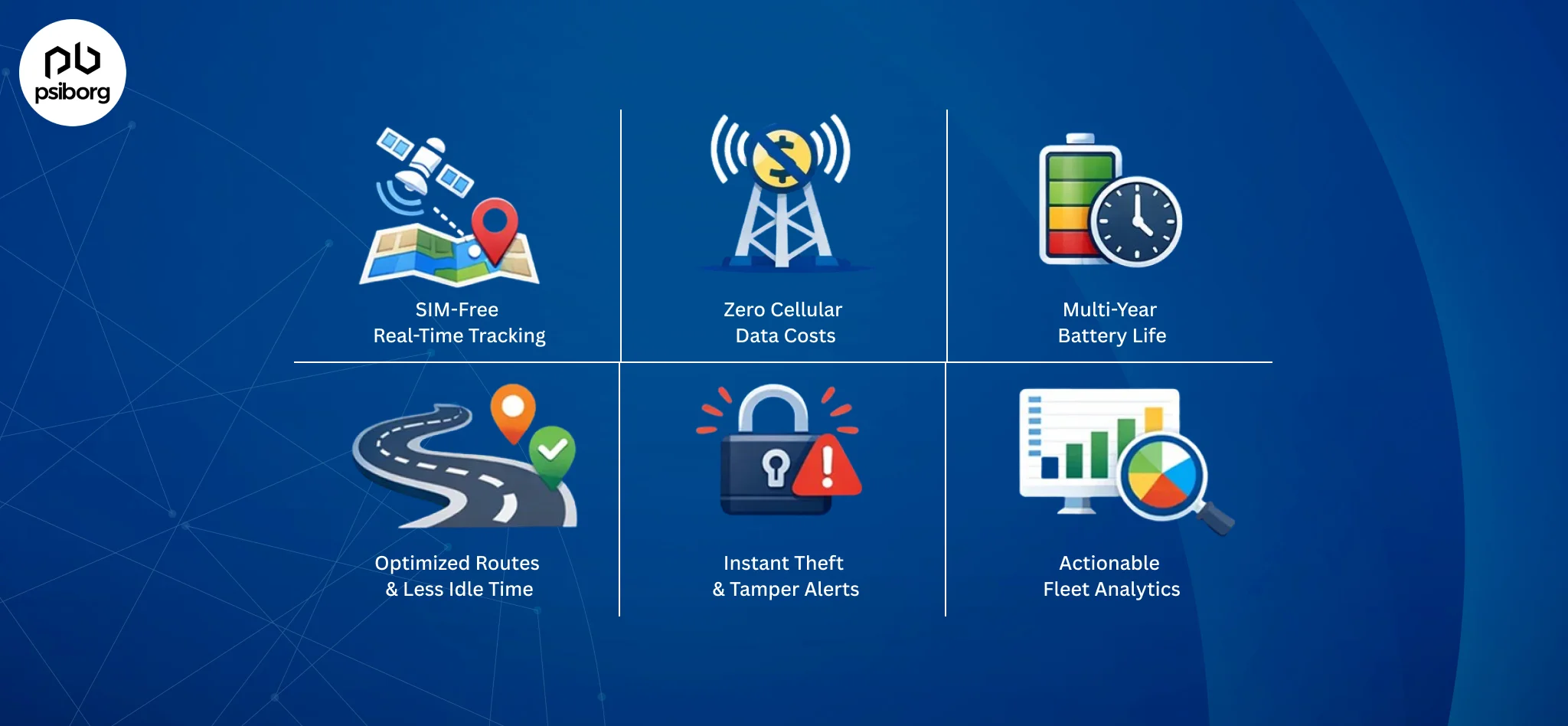
Benefits of LoRaWAN based fleet Tracking in industries
A LoRaWAN GPS tracking device delivers wide-area visibility at a fraction of traditional tracking costs, making it ideal for scaling fleet and asset monitoring across industries. By combining long-range connectivity, low power consumption, and smart data insights, businesses gain full control over operations while improving efficiency and profitability.
Key business benefits include:
- Real-time vehicle visibility across remote, urban, and industrial zones without cellular dependency
- Reduced connectivity expenses by eliminating SIM-based data plans
- Multi-year battery life that lowers maintenance and device replacement costs
- Faster deliveries through route optimization and idle-time reduction
- Improved asset security with instant alerts for unauthorized movement or tampering
- Actionable analytics for smarter planning, utilization tracking, and performance improvement
Explore how PsiBorg built a smart shipment tracking system that improved visibility, reduced delays, and optimized logistics operations, and discover what a custom IoT system can do for your business.
Now that we’ve explored the direct business value, it’s important to understand how LoRaWAN-based tracking stands apart from traditional tracking technologies businesses have relied on for years.
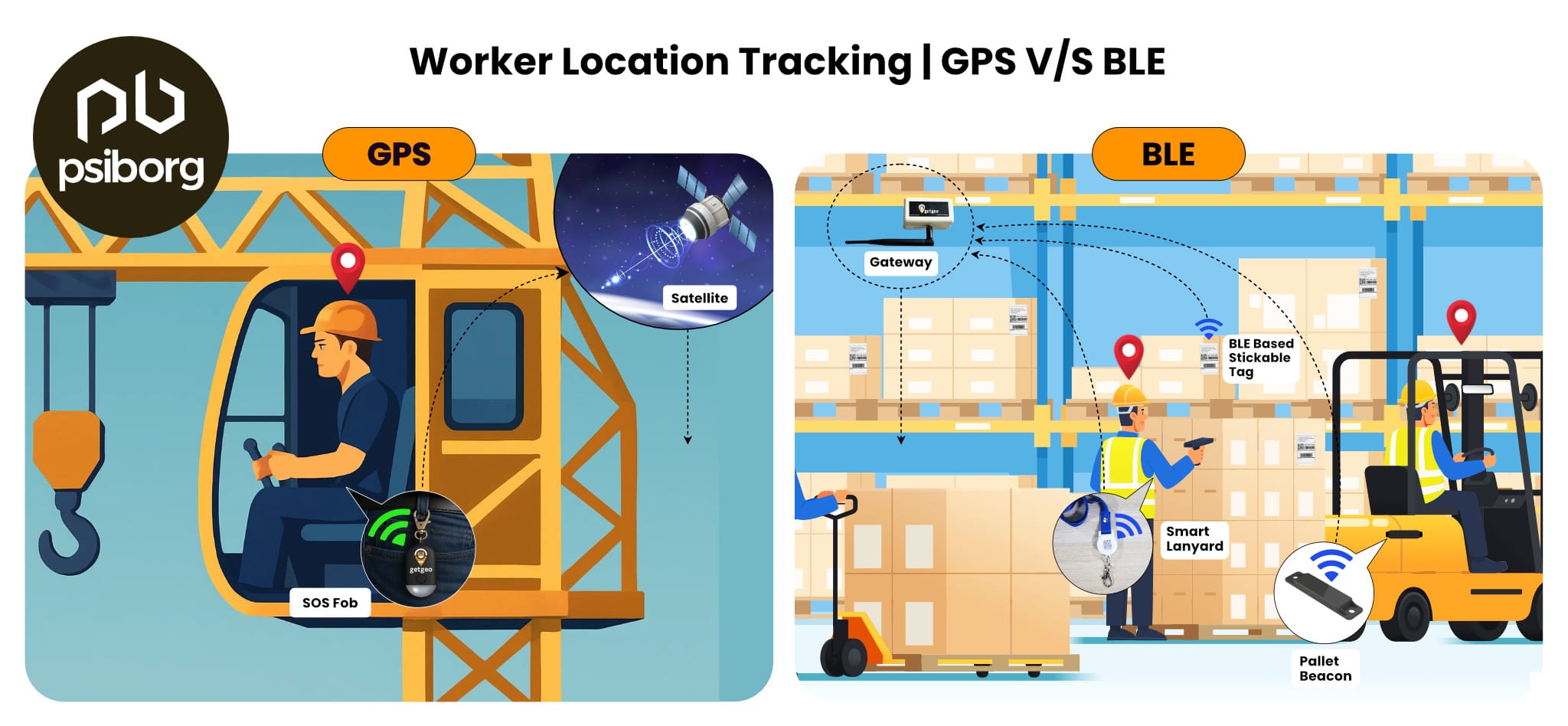
LoRaWAN GPS Tracking Devices vs Cellular VS BLE: A Practical Comparison
When evaluating vehicle tracking solutions, businesses typically compare LoRaWAN GPS tracking devices with cellular GPS trackers, satellite systems, and short-range technologies like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. Each has its place, but they differ significantly in cost, coverage, power consumption, and scalability.
Below is a clear, real-world comparison to help decision-makers choose the right fit.
Technology | Cost & Power Impact | Coverage Range | Best Use Cases | Key Limitations |
LoRaWAN GPS Tracking | Low operating cost, ultra-low power (multi-year battery life) | Several kilometers in cities, tens of kilometers in rural areas | Fleet tracking, industrial vehicles, remote assets, logistics | Not suited for high-frequency or large data transmission |
Cellular GPS (4G/5G) | High power use, ongoing SIM/data charges | Depends on mobile network availability | Real-time fleet monitoring in urban areas, delivery services | Expensive at scale, weak in remote or underground locations |
Bluetooth/BLE & RFID | Very low power and low cost | Very short range (centimeters to meters) | Warehouses, inventory tracking, indoor asset monitoring | No wide-area tracking, needs readers or gateways nearby |
Quick Takeaway:
- Choose LoRaWAN for wide-area, low-cost, long-term vehicle and asset tracking
- Choose Cellular GPS when constant live updates are essential and budgets allow
- Choose BLE/RFID for short-range or indoor tracking scenarios
After comparing tracking technologies, the next step for businesses is choosing a partner who can tailor these systems to real operational needs, not just off-the-shelf solutions.
PsiBorg’s Custom LoRaWAN GPS Tracking Solutions for Industrial Fleets
PsiBorg offers fully customized LoRaWAN GPS solutions that cover every stage of a vehicle or asset tracking project, from hardware design and sensor integration to cloud analytics, dashboards, and mobile apps.
Unlike generic products, PsiBorg’s solutions are built end-to-end to meet your specific fleet requirements, including real-time telematics, driver behavior analysis, route optimization, and secure data processing.
- IoT Devices & Firmware: PsiBorg designs rugged IoT hardware with embedded firmware optimized for long-range LoRaWAN connectivity and precise vehicle location tracking.
- Telematics & Fleet Management Solution: A tailored platform that combines GPS tracking with vehicle performance data to monitor routes, utilization, and operational efficiency in real time.
- Custom IoT Dashboards & Mobile Apps: Real-time fleet visibility, alerts, and analytics through user-friendly cloud dashboards built to match business workflows.
- IoT Cloud Integration: Secure backend systems that connect tracking data with enterprise platforms for centralized monitoring and automation.
PsiBorg’s domain expertise across sectors, from logistics to industrial automation, ensures high performance, long-term reliability, and faster time to value for fleet tracking deployments.
Ready to transform your fleet operations?
Contact PsiBorg today to design and deploy a LoRaWAN GPS tracking system that’s custom-built for your business goals, from proof of concept to full rollout.
Conclusion
A LoRaWAN GPS tracking device is transforming how industries monitor vehicles and assets by delivering long-range coverage, ultra-low power consumption, and cost-efficient scalability. From real-time fleet visibility and route optimization to enhanced security and data-driven decision-making, LoRaWAN-based tracking solves the limitations of traditional technologies while keeping operational costs low.
When paired with a customized, end-to-end IoT approach like PsiBorg’s, businesses gain not just tracking, but a complete intelligent fleet management ecosystem tailored to their needs.
FAQs
A low-power IoT device that uses GNSS and LoRaWAN networks to transmit vehicle location data over long distances with minimal energy consumption.
Modern multi-GNSS LoRaWAN trackers typically deliver location accuracy within 2–5 meters, even in urban or industrial environments.
Yes, LoRaWAN signals penetrate buildings and obstacles well, enabling reliable tracking across factories, warehouses, and large industrial parks.
Absolutely. Its long-range connectivity allows vehicle monitoring in rural highways, mining sites, and regions with limited cellular coverage.
It offers wide coverage, low operating costs, multi-year battery life, and reliable performance in harsh environments, perfect for large-scale industrial fleets.