IoT technology needs a continuous power supply, and batteries are one option but aren’t very economical. With the increasing popularity of the Internet of Things, several topics have emerged that we shouldn’t turn a blind eye to. One such heavily emerging topic is the power consumption of IoT devices.
You must have seen IoT devices getting power through batteries because they are generally deployed in remote locations and don’t have access to direct power supplies.
The power consumption issue has been there for a long time. Devices like mobile phones, watches, calculators, and remote controls are all powered by batteries.
However, IoT devices are a special set of devices that are foreseen to be able to function without any human intervention. Longer battery life is a repeated concern for people who are investing/buying IoT products.
With that in mind, let’s move ahead and discuss more about power consumption in IoT devices and how we can solve this problem.
THE PROBLEM OF IOT POWER CONSUMPTION
No doubt, IoT is the technology of the future and the best technology to ensure less electricity and energy consumption. But what about the big energy footprint that IoT will itself leave behind?
IoT has various applications. The use of IoT in smart building utilizes central power, but many other IoT devices require rechargeable battery support.
Here, in an IoT device, the level of power consumption heavily depends on its features and functions.
For instance, a resistance probe can consume up to 1 mA, a Bluetooth can draw energy up to 17.5 mA during the data transmission and retrieval process. If the device is put in sleep mode, this power draw can be reduced to 4 mA.
To be accurate, at present, there are mainly three ways in which energy is drained by IoT devices:
1. Data Centers
In an IoT ecosystem, data collection takes place through sensors, smart cameras, machines, and appliances. All the data collected by these sensors and IoT devices is stored and monitored in data centers that are majorly responsible for consuming large amounts of energy. Increasing demand for IoT will also increase power consumption.
2. Embodied Energy
Digital technology requires more power in manufacturing processes. The IoT technologies will impose a huge demand because it is expected that every person in the world will have at least 5-6 wireless devices.
3. M2M Communication
Machine-to-machine communication involves data backups, remote software updates, media backups, and data transmission among IoT devices. Although the majority of M2M communication consumes less energy, data-intensive products like wearable devices and smart medical devices drain huge chunks of energy.
WHAT ARE THE WAYS TO IMPROVE THE POWER CONSUMPTION OF IOT DEVICES?
To reduce the overall power consumption of IoT devices, there are several effective procedures. To understand these procedures and their effectiveness, we can divide these power consumption methods into multiple ways:
- Managing power consumption with software
- Managing power consumption with hardware
- Improving Power Consumption through Network Optimization
- Energy Harvesting
This is because there is no one way to achieve the perfect power consumption approach for IoT devices. There are different processes, designs, and development strategies that developers follow to decrease device power consumption and increase its lifespan.
But to tackle this power consumption issue, you first have to get answers to some major questions, like whether the device is fixed in one place or is moving. What type of data is it sensing and transmitting? And at what interval?
Let’s understand how we can optimize power consumption in different ways:
1. MANAGING POWER CONSUMPTION WITH SOFTWARE
One way is to optimize software for low power consumption. Programming the device in low-power and active modes will make a major difference in conserving battery power. Some new developments in low-power consumption, like various ultra-low-power sleep modes, offer more granularity than idle standby, doze, sleep, and deep sleep modes.
You can program your application so it can spend as little time as possible in the MCU’s “active” mode.
- It can also mean simplifying the applications or-
- Increase the amount of time the device consumes in low-power sleep states
- Raise the clock speed for faster processing and use of low-power timers for device wake-ups
- Taking into account the effects of firmware choices and updates
- Avoid excessive push notifications
- Consider smart monitoring and predictive maintenance.
2. MANAGING POWER CONSUMPTION WITH HARDWARE
In an IoT product, you have to select an energy-efficient microcontroller unit (MCU) for IoT applications. The programming needs might force you to opt for an 8-bit or a 32-bit MCU, but you have to consider the energy requirement as a prime parameter. Additionally, a microcontroller is not the only part that drains energy in the hardware design.
Another way to optimize power consumption is to use low-power sensors and nodes. In an IoT product, the sensor design can heavily influence the amount of power drawn from the device.
Besides this, you can also check the battery type or the passive components for current leakage. Some additional steps that you can take to optimize hardware energy are-
- Pick an MCU with different speeds and timer types, so you will have various ways to regulate the battery drain.
- Wherever possible, deactivate power to unused RAM
- Reduce the number of internal peripherals and deactivate unused peripherals
- Utilize wide power supply traces on the circuit board
- Make use of highly efficient switching regulators instead of low-dropout regulators.
3. IMPROVING POWER CONSUMPTION THROUGH NETWORK OPTIMIZATION
Selecting a connectivity solution can heavily influence the performance of the connected objects and their power consumption. For low-power-consuming IoT applications, there is LPWAN (LoRaWAN, LTE-M, and NB-IoT) for long-distance connectivity and BLE for battery-powered IoT devices.
Moreover, the connectivity distance between two nodes, topology, and message size can also influence the transmission time, thus impacting power consumption.
Some other ways of optimizing networks to improve power consumption are:
- Make sure that the device’s transmission frequency is as tight as possible.
- Don’t trespass on the neighbor’s bandwidth and abide through relevant standards
- Make sure that the device transmits information only when it has useful data.
4. ENERGY HARVESTING
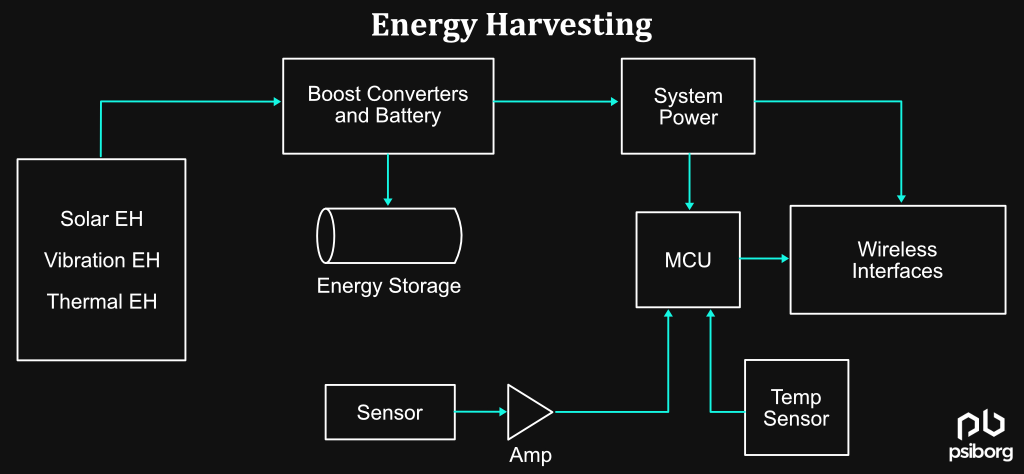
Energy harvesting can provide a significant, never-ending electrical energy supply obtained from the surrounding environment. This energy can replace a primary battery, depending on the application and available ambient energy. You can use this harvested energy to power the circuit.
An energy harvesting design will have three sub-functions: a circuit that can extract the energy from the transducer, an energy-storage element, and the harvesting management circuit, which will control the flow of energy into the battery.
Nevertheless, efficient power consumption has always been the biggest challenge for IoT because IoT devices need constant power, and based on the function of the device, the amount of power drained can be small or large.
While there are some power-saving tips that we have mentioned above, through them, you will be able to maintain the power of the device.
Moreover, power optimization needs a systematic approach. If you want to design a device that uses less power, do not ignore the fact that efforts to reduce power consumption can lead to undesirable performance results in various areas of the device.
So, it’s better to let the experts handle this aspect. We are a leading IoT solution-providing company and can solve the power consumption in IoT devices by developing a fully functional and efficient IoT device.
Take your time to weigh every option and their pros and cons, or let us handle all that for you.
PsiBorg will do both, find the answers to your queries, and do all the heavy lifting for you.
FAQ
Measuring power consumption in IoT devices requires a test system and simulation tools. The system comes with an internal preamplifier built into the spectrum analyzer. This is for continuous power monitoring.
However, you can use a power meter or multimeter to measure the current and voltage across the device. Further, multiply the values to calculate the power in watts.
Wireless communication modules like WiFi or cellular modules are generally considered the largest power-consuming component in an IoT device. This is because transferring and receiving data wirelessly requires significant energy, thus increasing the overall power consumption of IoT devices.