As air pollution levels rise and environmental degradation increases, urban spaces are looking for ways to tackle this. One of the key ways to control air pollution in cities is to reduce vehicular pollution. Electric vehicles (EVs) are an innovative step in this direction. And IoT for Electric Vehicle can help companies to get various insights helping them to improve customers’ experience.
Electric vehicles are hi-tech machines that bank on a lot of data to deliver the most optimum performance. The performance parameters include monitoring of speed, acceleration, mileage, battery management, charging, fault alert and predictive maintenance systems. Let us understand in detail the aspects of an IoT Electric vehicle management system.
ROLE OF IOT IN ELECTRIC VEHICLE MANAGEMENT
Let us look at the role played by IoT in the management of Electric Vehicles:
BATTERY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
The basic functions of the Battery Management System (BMS) are to monitor and control the battery processes such as the charging and discharging cycle, thereby ensuring battery health, and minimizing the risk of battery damage by ensuring that optimized energy is being delivered from the battery to power the vehicle.
The monitoring circuit in BMS monitors the key parameters of the battery like the voltage, current, and temperature during both charging and discharging situations. It estimates parameters such as the power, State of Charge (SoC), and State of Health (SoH) and ensures healthiness based on the measurement. Internet of Things (IoT) plays a major role in monitoring and control, also it enables the remote data logging facility for battery parameters, conditions, etc.
EV manufacturers are increasingly opting for high-quality Li-ion battery packs due to their longer life and better range of high energy density. Besides these benefits, there are some drawbacks too.
In scenarios where the battery malfunctions, the onboard sensor data obtained through IoT can help in managing the challenges. Then, these can be run through AI-based models for performance evaluation.
Tests can be conducted on some Li-ions to assess the patterns of partial & complete charging and discharging and the thermal stress pattern. Models are characterized using the data collected from each step. These are integrated with AI before deploying on a server. The EV sends crucial sensor data to the server, providing insights on the next course of action and performance. We can say that the EV’s state is monitored by the server.
SAFETY AND SMART DRIVING
The use of IoT would also enable real-time monitoring of the vehicles and their key components. It also helps in preventive maintenance offered by the technology making the users find it more reliable.
IoT devices embedded in EVs can provide users with the following features:
It can gauge the absolute and relative parameters of the driver, such as speed, acceleration, and others, for providing real-time tips to ensure better performance.
Theft can be prevented through real-time tracking, geo-fencing, and immobilization. Thus, there will be enhanced safety and security to reduce the dependence on insurance.
It will monitor the vehicle performance data, based on which the EV and battery OEMs can improve the products. The parameters include a range for each charge, utilization of a vehicle, performance differences based on geography, weather conditions, age, and alteration in range for each charge over a certain period.
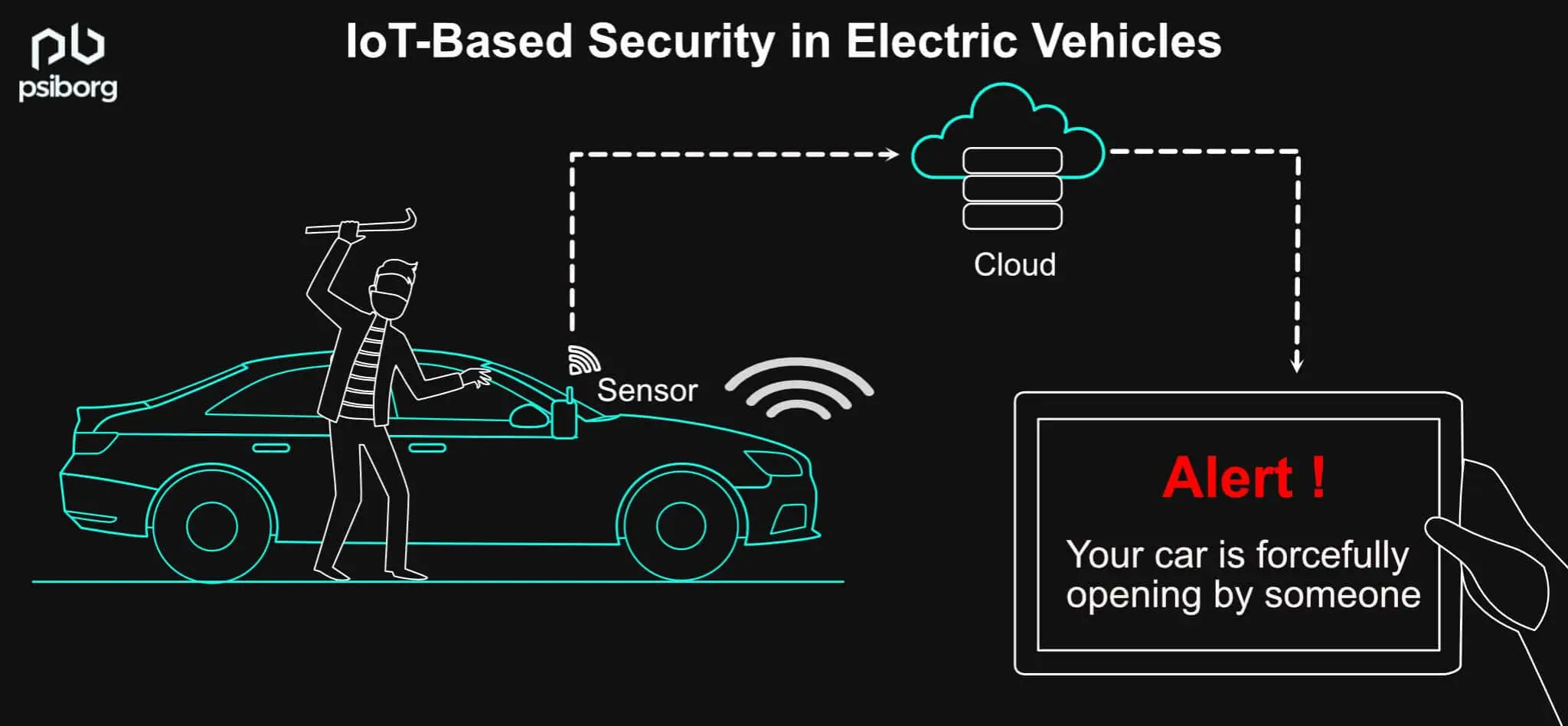
FAULT ALERT AND PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE SYSTEM
Being a high-tech machine, an electric vehicle is bound to experience technical glitches. IoT-based fault alert systems help to alert vehicle drivers regarding the EV faults, giving them time to act and address them.
Despite the fact that EVs are carefully designed, there can be situations where the components might falter or fail. In order to predict this, AI algorithms and remote IoT data can play a key role. This helps in alerting the EV users ahead of time to fix any possible issues or avert a total breakdown. This will lead to a better customer experience as they will find it to be reliable.
Keeping in view the overall temperature and moisture conditions in various geographies, monitoring the remote performance is extremely important. This will not just help in resolving the issues quickly but also provide a sense of comfort and security to the users about the EV’s health through predictive diagnosis
TELEMATICS DATA
With the help of IoT-based telematics technology, data is collected when connected to vehicle sensors and it can be rapidly displayed through widgets, send instant notifications, and generate automatic reports.
Here are the beneficial factors of using telematics for remote monitoring electric vehicles:
BATTERY USAGE DATA
Electric vehicles that have telematics enable users to track real-time data of battery usage. This data analysis provides insights that help to improve battery life. It also allows monitoring of vital parameters like voltage, current, and temperature to avoid battery breakdowns. Using this IoT device battery usage of EV can be recorded and transferred to a remote server that can allow you to personalize the battery configuration and improve your best charging practices.
CHARGING REPORT
The use of telematics in electric vehicles helps to generate reports on complete charging sessions of the vehicles that might have gone through their lifetime. The charging report includes the time duration, location of the charger station, and percentage of charge received by the vehicles.
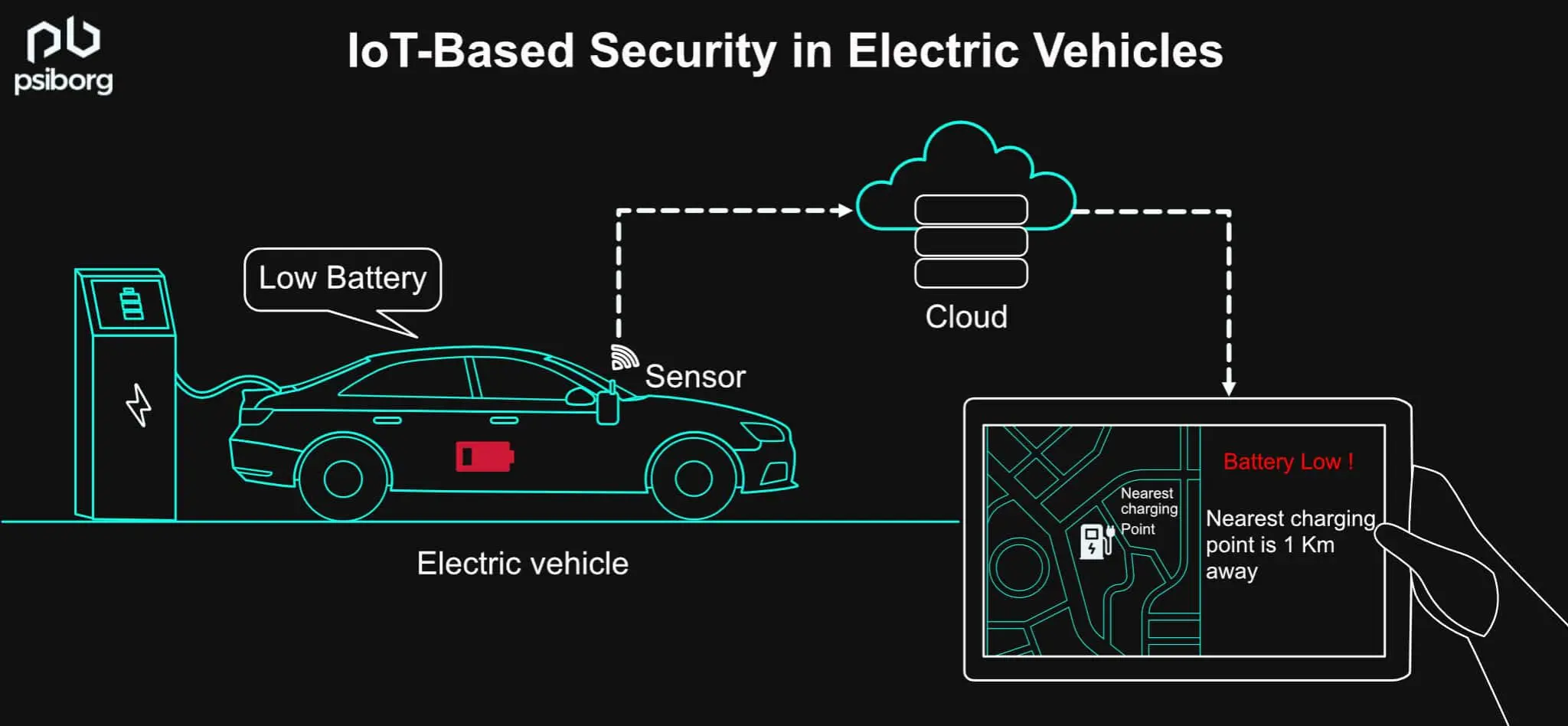
NEARBY CHARGING STATIONS ALERT
Electric vehicle users face challenges like knowing their state-of-charge(SOC) to plan when and where to charge. EV Charging Management System notify the user regarding the low battery level of the vehicles along with the location of nearby charging stations which prevents bricked vehicles.
DRIVER BEHAVIOR DATA
Electric vehicle remote monitoring system with telematics not only monitors and analyzes the data of electric vehicle performance but also concentrates on behavioral data of EV drivers. Telematics offers instant feedback to fleet managers through IoT smartphone apps on driver behavior changes to improve vehicle safety.
BENEFITS OF IOT IN ELECTRIC VEHICLE MANAGEMENT
The integration of IoT in the electric vehicle industry is currently the topic of discussion among industry leaders because of its various applications and benefits.
Below is the list of benefits that IoT offers in the EV industry:
– IMPROVED USER EXPERIENCE
With mobile apps or vehicle dashboards, car drivers can obtain accurate and real-time information about their vehicle’s charging status, battery range, and maintenance requirements. All this type of information will give users a smooth driving experience.
– INCREASED PRODUCTIVITY
The sensors embedded in several vehicle components give real-time data regarding batteries, charging systems, energy consumption, and vehicle performance. These obtained data can be analyzed to identify patterns and anomalies, thus providing you with scope for improvement.
– LOWER DOWNTIME
The sensors used in the system will identify potential issues by continuously collecting and analyzing data from vehicle components before any significant problem occurs. This will give you time for timely maintenance/repairs, resulting in reduced downtime.
CHALLENGES IN ELECTRIC VEHICLES MANAGEMENT USING IOT
While there are some significant benefits to integrating IoT technology into the EV industry, it is also important to understand the challenges associated with IoT in the EV industry. Here we have listed some challenges that the EV industry might face:
CYBERSECURITY
The use of the high amount of data and the fact that all of it is sent over a network makes this data vulnerable to cyber-attacks and data thefts. Therefore, the IoT networks that EV system data is based on should be strengthened and made more foolproof
HIGH COST
IoT systems in EV are pretty advanced and have high installation and running costs. The future holds the possibility for more R&D in this area to reduce costs.
THE FUTURE OF IOT IN THE EV INDUSTRY
The growing EV market is in need of consistent and reliable services, and IoT technology is the center of this.
The use of IoT technology will facilitate data exchange and effective remote monitoring and management. According to the report, it is estimated that the connected car and IoT industries will be worth $42 billion by 2024, with a CAGR of 9.2%.
Another report by Allied Market Research states that the wireless charging system segment is estimated to experience the fastest growth, at a 28.8% CAGR, from 2020 to 2030.
This indicates that IoT technology is here to stay in the EV industry and will only become more prevalent in the coming future.
TO FINISH UP,
IoT-enabled EVs that can be charged and monitored have started entering the market. In our view, the IoT opportunity is immense in the field of electric vehicles. EV components are already connected, like charging stations and sensors. Therefore, it would be easy to integrate vehicle hardware into the IoT ecosystem.
Moreover, Integrating renewable energy sources and providing real-time data on energy usage enables predictive maintenance.
If you are in the EV industry and want to leverage the power of IoT to improve your business operations. Then we suggest you, have a call with us.
PsiBorg , an IoT product development company, specializes in designing and fabricating high-end IoT systems for electric vehicles. Do reach out to us for more information on this
Also, Read: AUTOMOTIVE EMBEDDED DEVICES
FAQ
Yes, once the EVs are added by the owner/admin to the IoT Dashboard, we can monitor and manage various aspects, for instance, battery management in electric vehicles, simultaneously.
Yes, with IoT, you can track and store historical data of electric vehicles (EVs). Through sensors and IoT connectivity, the system can record information such as charging history, battery performance, and vehicle running patterns. This historical data can be further analyzed by the EV owner for maintenance and optimization of the electric vehicle.
The cost of implementing IoT for electric vehicle monitoring includes the cost of the devices, connectivity, infrastructure for data storage and analysis, and ongoing maintenance. In addition, there are the costs of software development and integration with existing systems. These costs can vary depending on the complexity of the monitoring system and the desired functions.