India ranks second in on-farm output worldwide, and around 42% of India’s population is employed in the agriculture sector. A sector that has such a vast impact on the country, just depending on climatic conditions and manual methods of farming, seems a little outdated, and with the thriving world population, a change in the system is required now more than ever.
So how long are you going to rely on plows, wheelbarrows, and shovels when drones, self-driving cars, and virtual reality are no longer a fantasy?
This is why we think smart farm sensors should be used more widely with an introduction to smart agriculture.
The agriculture space has undergone lots of changes in the past few decades, from GMOs to pesticides, and has become more technology-driven. So, it’s only logical to say that IoT (Internet of Things) and agriculture environmental sensors are the future of farming.
Smart agriculture using agro sensors has started to launch in markets to make agriculture more “smart,” giving us a reason to write about this.
In this article, we will give insights on IoT-based smart agriculture and sensors used in smart agriculture.
So, let’s begin!
WHAT IS SMART AGRICULTURE?
There are many ways to introduce technology to agriculture, but when we make use of wireless sensor networks in agricultural fields, it is known as smart agriculture. The farming sensors are utilized to collect environmental and soil metrics and provide them to farmers so that they can make informed decisions to improve every aspect of their work, be it livestock or crop farming. The ultimate goal is to increase the quality and quantity of the crops while reducing waste and optimizing the human labor that is used.
WHAT ARE SENSORS?
Sensors in IoT solution development are all we are going to talk about in this article. So let’s get an idea of it first. A sensor is a device that senses and responds to certain inputs, such as movement, light, pressure, heat, or moisture and converts them into a human-readable representation.
For example, you have a plant at home and are not sure when to water it. So, you fix an agro sensor in the plant pot. The sensor will detect when the soil is dry or wet. If it’s dry, the sensor will detect it and send you a signal on your mobile phone saying, “Please water the plant.”
This is how the sensor works.
IMPORTANCE OF IOT SENSORS IN AGRICULTURE
There are countless benefits to smart farm sensors in agriculture. Some of the important plus points of using agricultural environmental sensors are:
Global Connectivity
Cellular networks (3G, 4G LTE-M/NB-IoT), LoRaWAN, and Bluetooth Tracking Solutions ensure smart farming tools and IoT farming tools collect the data you need, anytime and anywhere.
Inputs/Outputs
Connects a range of farming GPS devices and switches to fit any application, be it gate open/close, water meters, pump running/not running, and more.
Environmental Monitoring
One can connect IoT sensors used in agriculture, such as temperature and moisture sensors, for environmental monitoring applications.
Rugged and Waterproof
The use of sensors in agriculture can ensure fine dust, high-pressure spray, submersion in water, and extreme temperatures.
Run Hour Monitoring
Smart agriculture tools like sensors and tracking devices capture run hours based on movement to understand and optimize asset utilization.
Easy Install
There are multiple installation options for covertly securing agricultural sensors and GPS devices.
IMPORTANCE OF SOIL HEALTH IN AGRICULTURE
Soil is the foundation of productive, sustainable agriculture. Soil health” can be defined as “the state of the soil being in sound physical, chemical, and biological condition, having the capability to sustain the growth and development of land plants.”
The traditional method of testing soil health include: –
- Register on the soil health governance portal.
- The team does soil collection.
- Soil testing is done in the laboratory.
- The soil health report is provided in 15-20 days.
- Accordingly, fertilizers are recommended.
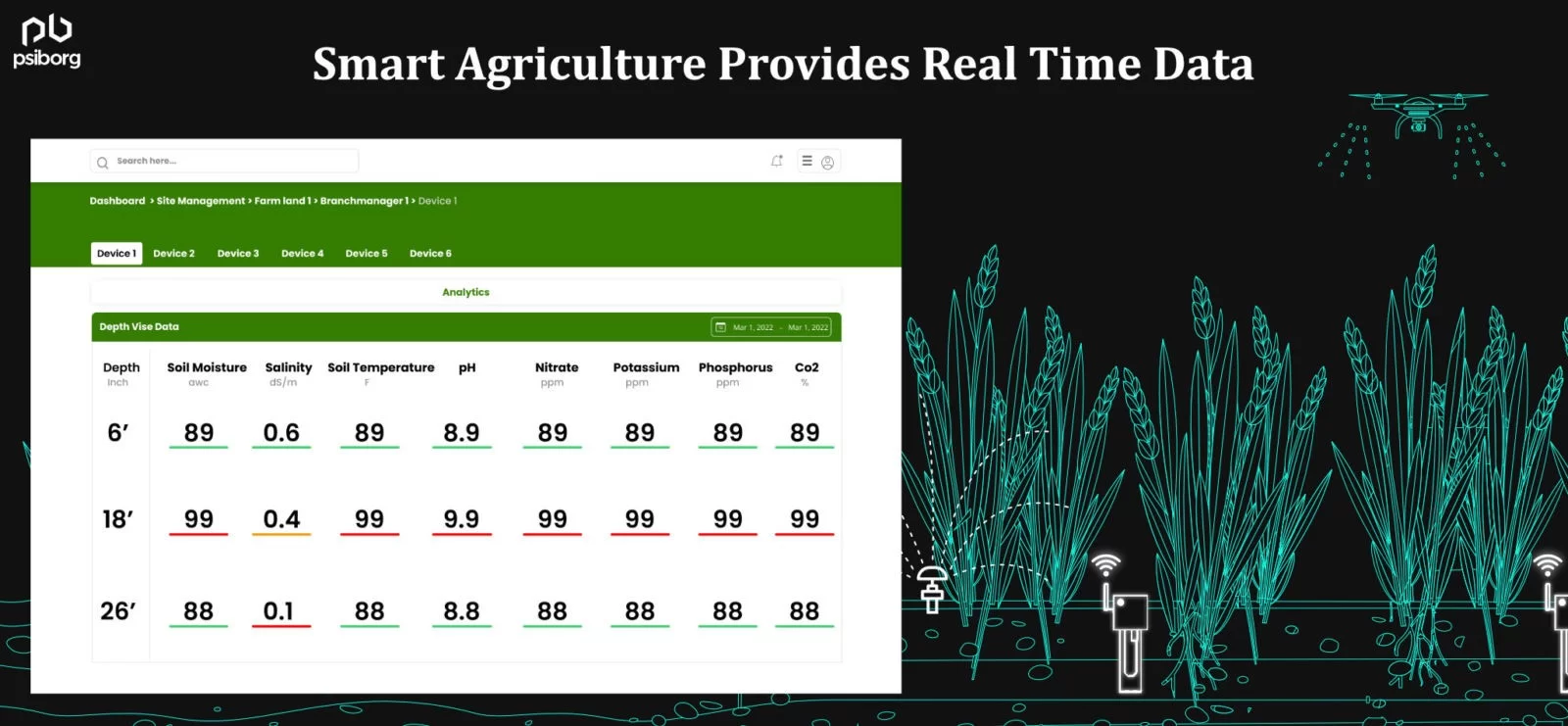
With Smart agricultural sensors, the soil health data is fetched and analyzed. This data is logged in real-time, and comparisons of soil health reports are done for weekly, monthly, or yearly data and can be seen on the app directly, without wasting any time.
This is done using soil health monitoring system that provide data on parameters that help in analyzing soil health. Now the question arises:
WHY SHOULD WE BE USING SENSORS IN AGRICULTURE ANYWAY?
One word, data. The biggest advantage these sensors have is the huge amount of data they can collect. From the weather conditions to the soil quality to the crop’s growth process, collecting the relevant data can be a game-changer. No doubt, the farmers know best about the crops and their lands, but sometimes the problems can be hidden and unpredictable, and that is where these sensors help.
These sensors monitor the whole system 24×7 to provide the farmers with the necessary data, which helps them make informed decisions that are going to help them in better cost management, waste reduction, and water conservation due to their increased control over production, which is eventually going to help them flourish their agriculture business and is going to result in higher revenues.
The UN projects that the world’s population will reach about 9.7 billion by 2050, which will cause global agriculture production to rise by 69% from 2010 to 2050. To meet this growing demand, farmers will have to take advantage of IoT solutions that can increase their productivity. IoT is all set to push the future of agriculture to the next level. IoT implementation has already become common for farmers in many countries and will soon become a standard practice in India too.
Suggested Reading: Precision Farming Using IoT
TOP 5 SENSORS TO USE IN SMART AGRICULTURE
Now that we know farming sensors are highly useful for business, let us take a look at some of the useful agro sensors.
SENSORS TO MONITOR CLIMATE CONDITIONS
As the weather is one of the few parameters not in our control, weather stations are probably the most popular smart agriculture gadgets. Weather stations combined with temperature and humidity sensors play an essential role in smart agriculture to provide ambient condition monitoring. These provided measurements can be used to map climatic conditions and choose the appropriate crops.
Weather can also be forecasted directly by integrating APIs into the sensor system gateway. This way, precautionary measures can be taken against any undesirable climate conditions.
The favorable environmental conditions for growing a certain crop are measured through the:
- Light Intensity Sensors
- CO2 and O2 sensors
- Wind Speed
SENSORS TO MEASURE SOIL PROPERTIES
There are various sensors that are used to check Soil quality parameters, such as
- NPK value
- Moisture level
- Soil Conductivity
- PH value
- Soil Temperature
This data on soil is collected and analyzed, which helps recommend favorable crops as per the Soil Health. The data for recommending crops is fed to the Smart Agriculture system, and with ML & AI system is made intelligent.
SENSORS FOR PESTICIDES
While pesticides are necessary for keeping crops pest-free, putting in the right amount is extremely important. Putting an excessive amount of pesticides can be harmful to the plants and can contaminate the soil and water. Furthermore, with repeated use of excess pesticides, the insects and bugs can become resistant to them, which will only force the farmers to use heavier pesticides.
Image-capturing sensors have proven to be cheap but, at the same time, a very efficient method of pest detection. Based on the images, the farmers determine the area of the infestation and take steps to remove it by spraying pesticides in specific areas.
Gas sensors are another popular way to detect pests. Plants release specific volatile gases when stressed. The chemical compounds released differ for each cause of stress. Hence, the compounds that are released in the case of a pest attack can be studied beforehand and can be used to identify such attacks.
SENSORS FOR CATTLE TRACKING AND TRACEABILITY
Just like sensors used in smart agriculture for monitoring the soil, there are devices that can be used for livestock monitoring. IoT sensors attached to animals can provide information about their health, well-being, and physical location. GPS satellites are used to determine latitude, longitude, and altitude. Additionally, geofencing is incorporated by the caretakers to keep track of their livestock. It is a location-based service that sends alerts when an animal leaves their designated area. This also reduces the cost of the staff required.
SENSORS TO MEASURE SOIL COMPRESSION
The last sensor to secure its place in the list of the top 5 agro sensors is the sensor for measuring soil compaction. Mechanical sensors can be used to measure the resistance of the soil by applying resistive forces. These mechanical sensors use load cells or strain gauges to determine the force that roots exert to absorb water. The data collected is used to optimize tillage methods and water inflow.
The types of sensors for the above-mentioned properties are:
- Optical sensors: These sensors use light to measure soil properties and have been developed to determine the clay, organic matter, and moisture content of the soil.
- Electrochemical sensors: These sensors provide information about the content of O2, CO2, and other essential gases present, along with pH and soil nutrient levels. Sensor electrodes penetrate into the soil to detect specific ions in the soil. Determining essential nutrients can provide the best conditions for the crops to grow.
- Dielectric sensors: These sensors assess the moisture content in the soil. The crops can be better irrigated once we know the moisture in the soil. This leads to better water management. Dielectric sensors can also be used to determine the pH of the soil.
Data collected from all the different agricultural sensors is to be analyzed and visualized to serve different purposes. These data are sent to the IoT Dashboard which collects the data in real-time and converts it into human-readable form. Data collected in real-time helps farmers make informed decisions.
FEATURES OF THE SMART AGRICULTURE SYSTEM ARE
With the sensors installed in the agricultural field, farmers get information about their fields on their phones. Let’s understand in detail what are the features provided by smart agriculture:
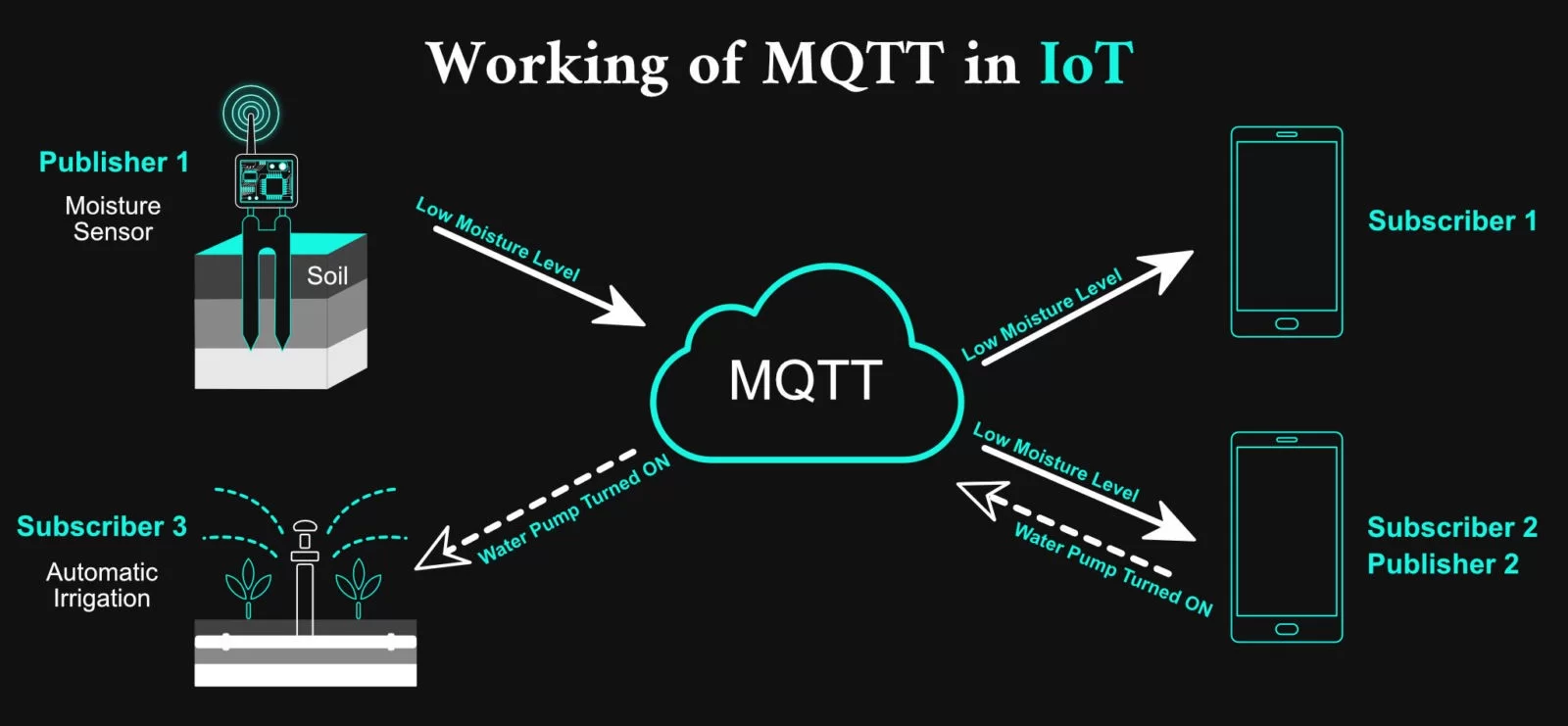
AUTOMATIC IRRIGATION OF SOIL
With a lack of fresh water, it is important to use the water provided wisely. Putting sensors to detect the moisture in the soil is going to use the water effectively and result in a better yield of crops. This system consists of a water pump that sprinkles water based on the data provided by the sensor about moisture, temperature, and humidity. It helps in saving water as well.
With the use of the MQTT protocol in Smart Agriculture solution, the command is sent to the sprinkler actuator to Turn On the sprinkler, if the moisture level goes down a threshold value. In the below image, it is shown how MQTT helps in Smart Agriculture.
SOIL NUTRIENTS DATA
Soil provides the nutrients required for crop growth. Chemical and physical properties of the soil, such as moisture content, temperature, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium content, heavily affect the crop’s yield. In cases of deficiency of these nutrients, the farmers put in fertilizers, and often they put more or less than required. Hence, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium sensors are used to monitor soil health so that farmers can apply fertilizers whenever required and in the right amount.
AGRICULTURAL DRONES
Drones are equipped with sensors and cameras for imaging, mapping, and surveying purposes. There are ground-based and aerial drones. Ground-based drones are bots that survey the field on wheels. On the other hand, aerial drones are flying robots that are either remotely controlled or can fly automatically through software-controlled flight plans. Insights on crop health, irrigation, spraying, planting, soil, and fields can be drawn from the data collected from the drones. After the drones survey and collect the data, they are taken to a nearby lab to be analyzed.
SMART GREENHOUSE
Greenhouse farming helps enhance the growth of vegetables and fruits. Greenhouses control the environmental parameters through manual intervention. This leads to production loss, energy loss, and more labor costs with less effectiveness. A smart greenhouse that is built with the help of IoT intelligently monitors and controls the climate, eliminating the need for manual intervention. Different sensors are used to measure the environmental parameters, and the environment of the greenhouse is controlled accordingly. Temperature sensors used in agriculture monitor the greenhouse crop, prevent diseases, and help in planning seasonal crops.
PREDICTIVE ANALYTICS IN AGRICULTURE
Crop prediction according to the weather, soil requirements, etc is very important for the farmer to decide future plans regarding the production of crops. To predict the production rate of the crop sensors, collect information regarding the soil, temperature, pressure, rainfall, and humidity. All of this data is collected on a dashboard and analyzed for the farmer to make an informed decision about which crop to produce.
In conclusion, we would like to say, that technology has benefited many sectors in India. And it is high time the agriculture business benefits from it too with the help of the sensors used in smart agriculture.
Also Read: WHERE DO IOT-BASED SMART AGRICULTURE SYSTEMS USE SENSORS?
Implementing IoT in the agriculture business can bring about an extremely positive change. If you are looking to implement such farming solutions, then look no further. We at PsiBorg, an IoT Product Development company, can bring about the changes you want.
FAQ
The sensors that are used in precision agriculture are generally mechanical soil sensors that measure soil compression, electrochemical sensors that collect and process soil chemical data, and soil moisture sensors. All these soil sensors are used for soil nutrient detection, and they supply accurate details needed for agriculture.
The pH sensor used in agriculture is a device that measures the acidity and alkalinity of the soil. They work by measuring the hydrogen ion activity inside the soil. These pH sensors in smart agriculture provide critical feedback regarding soil nutrient deficiencies. This helps in deciding the type of fertilizer to add to the soil.
The use of soil moisture sensors helps farmers with irrigation scheduling by showing data about how much and when to water the soil for a specific crop. This way, farmers can provide neither too much nor too little, just sufficient water for the crops.
In smart agriculture, the use of irrigation sensors is part of the smart irrigation system. The irrigation sensors gather and transmit data about the plants and the surrounding soil. This is done to inform the farmers about how much and when the crop need’s water.
As the name suggests, the chlorophyll sensor measures the concentration of chlorophyll in plants. Chlorophyll is the green pigment in plants that creates energy from light.
Plant chlorophyll levels can be detected earlier and more accurately with the chlorophyll sensors, improving crop yield.