In this blog, let’s discuss wireless sensor networks vs. Ad hoc networks and understand the difference between wireless sensor networks (WSN) and ad hoc networks.
Both WSN and ad hoc networks are considered emerging technologies that have the potential to transform numerous industries and become an essential part of our daily lives.
Let me explain WSN and Ad Hoc networks first:
WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS (WSN)
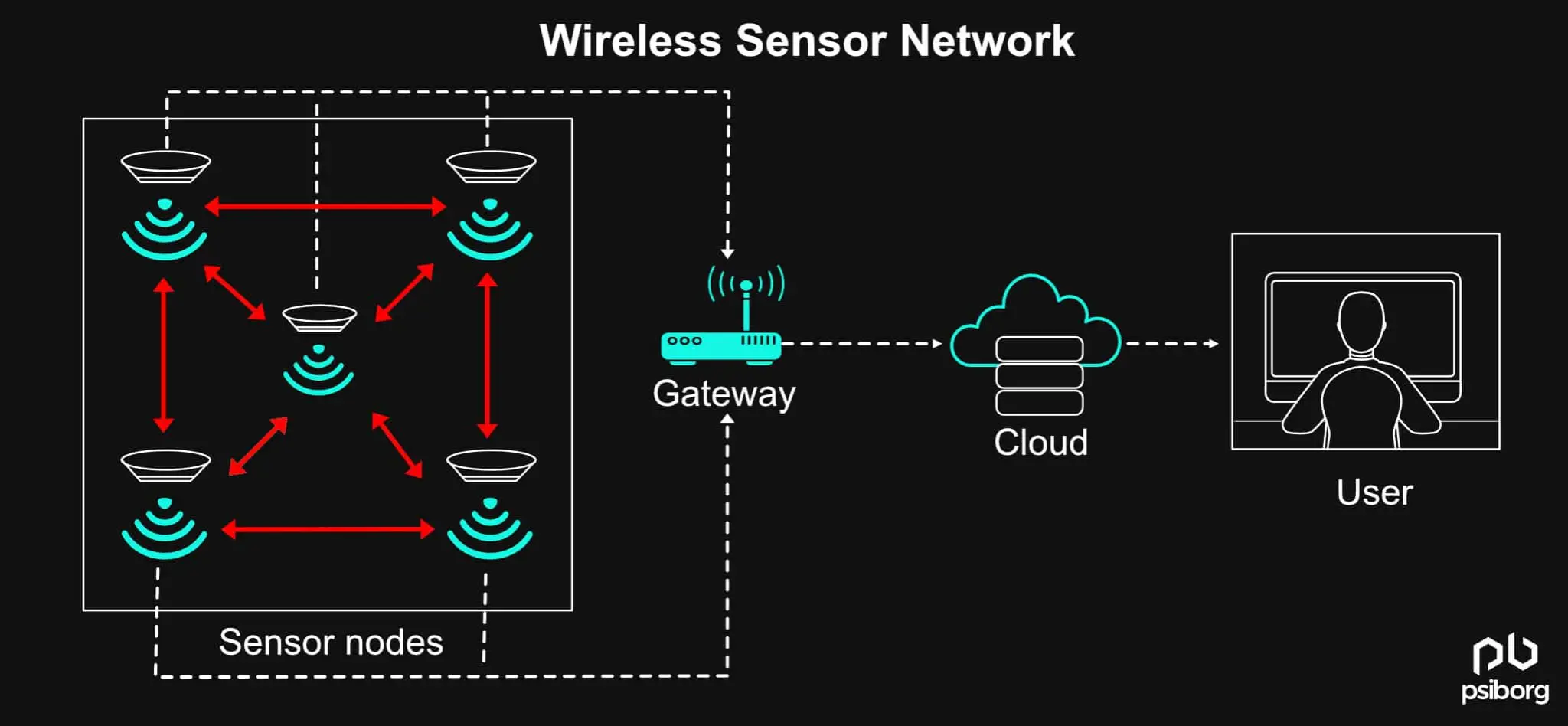
The wireless sensor network is a group of sensors that can communicate wirelessly. The aforementioned groups of sensors can communicate within their communication range and are hence capable of operating in changing environments.
Let’s compare the internet with a human’s Central Nervous System (CNS). Wireless sensor networks are like sensory organs that sense the surrounding environment and gather information to process it further.
Therefore, WSN is a combination of a large number of sensor nodes. The following sensor nodes collect, process, and transfer the data to the users.
The nodes mentioned above can either be stationary or mobile.
A few applications of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN):
- Environmental Monitoring
- Health Care
- Positioning and Monitoring
- Disaster prevention and relief
- Smart Agriculture System
- Infrastructure control
- Security
- Logistics
AD HOC NETWORKS
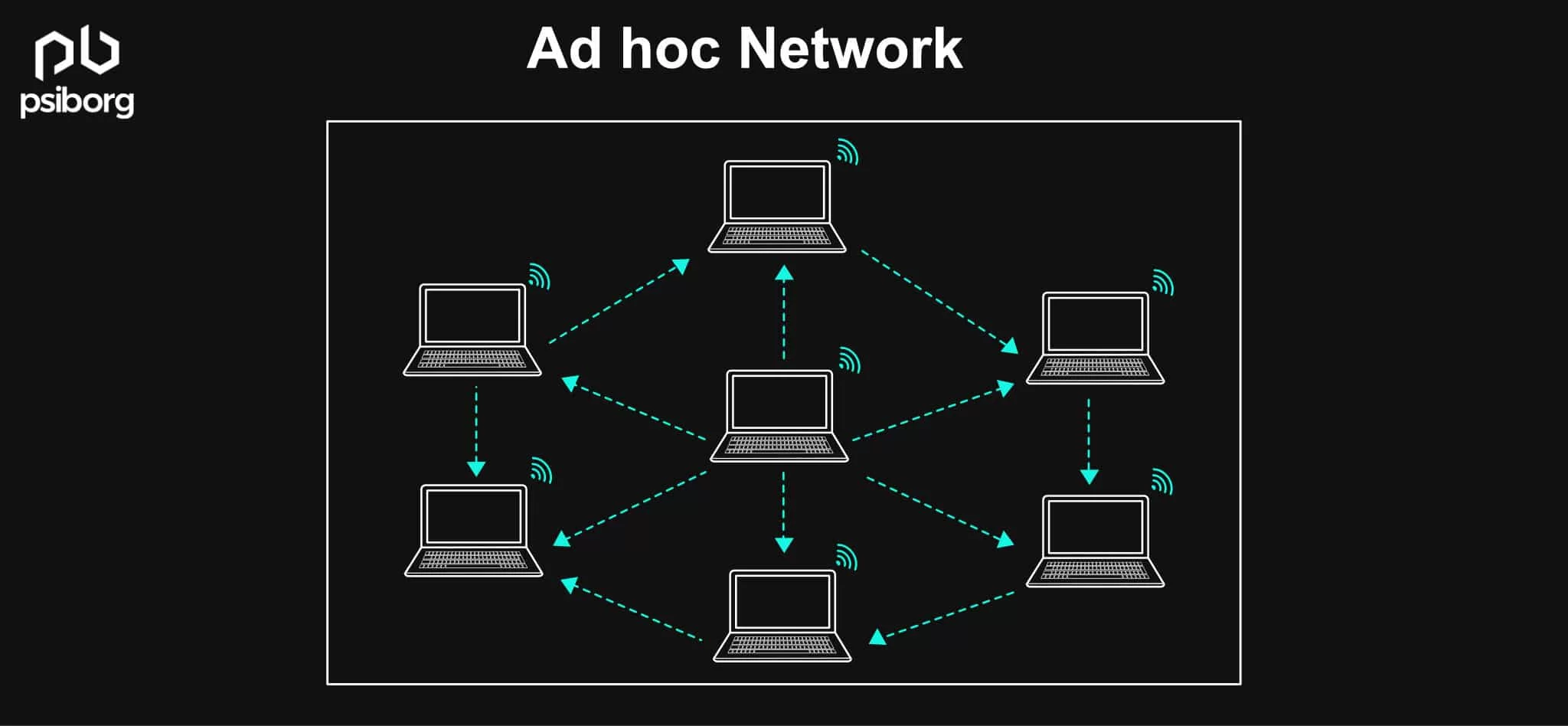
Ad hoc networks are mainly for data communication and have no sensing ability. These are self-configuring networks of wireless links connected to mobile nodes.
The aforementioned mobile nodes convey information directly to each other without any access points; that’s why they are infrastructure-less.
They create an arbitrary topology, where the routers move randomly and arrange themselves as required.
If we take the same example of the human Central Nervous System, the Ad hoc networks work like nerve endings to communicate with the brain and body.
However, ad hoc networks were developed by the defense forces in the early seventies to comply with military frameworks. These networks have now also proven useful in the commercial and industrial fields.
Some common applications of Ad hoc Networks are:
- Data Mining
- Military Battlefield
- Commercial Sector
- Personal Area Network or Bluetooth
- Emergency and temporary communication
WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS VS. AD HOC NETWORKS: DIFFERENCES
Ad hoc networks are primarily designed for data communication; wireless sensor networks, on the other hand, are designed for data communication, data collection, and data storage
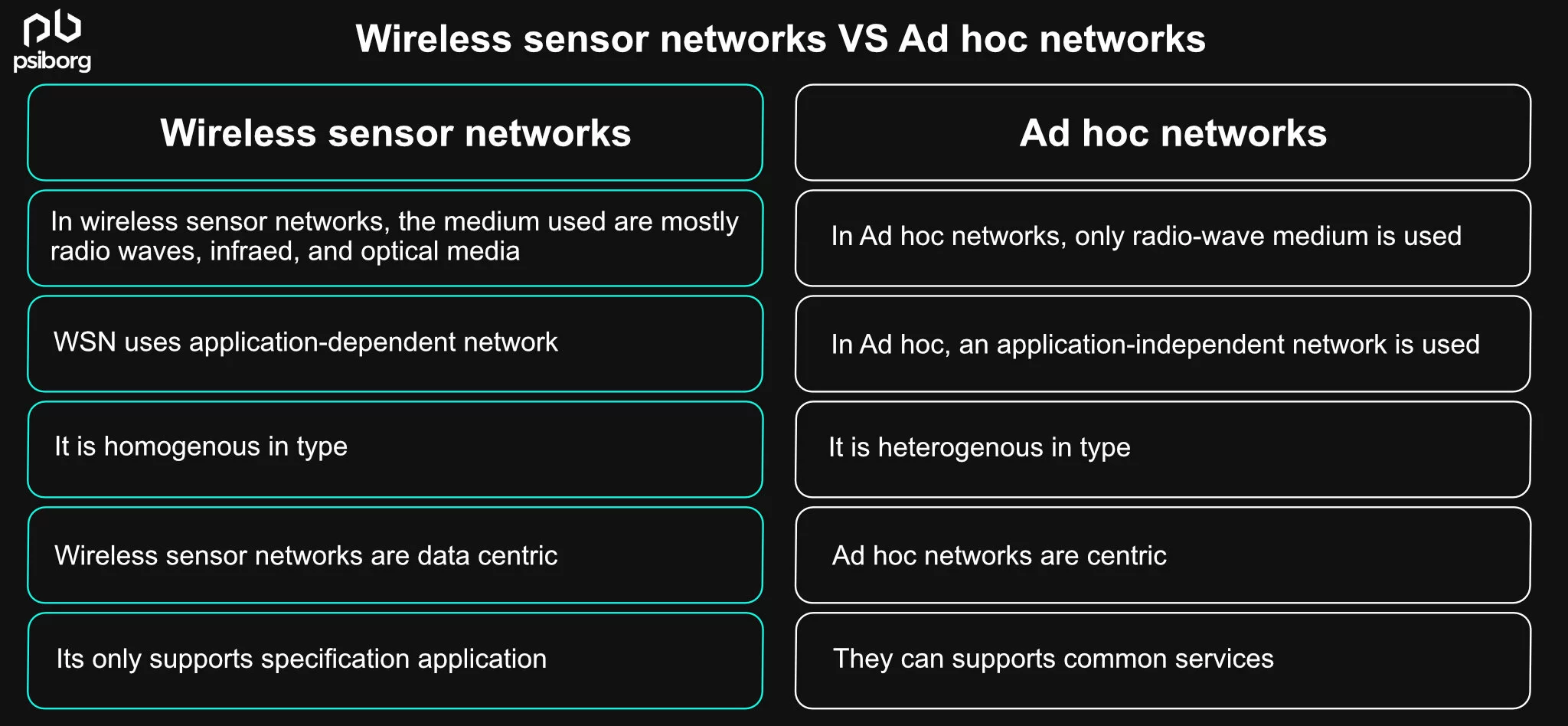
The following comparison table will help you gain a better understanding of wireless sensor networks vs. Ad hoc networks.
| Wireless Sensor Networks | Ad hoc Networks |
1. In wireless sensor networks, the mediums used are mostly radio waves, infrared, and optical media. 2. WSN uses application-dependent network 3. It is homogenous in type 4. Wireless sensor networks are data-centric. 5. In WSN, the traffic pattern is any-to-any, many-to-one, many-to-few, and one-to-many. 6. It only supports specific applications 7. Nodes are limited to sensor nodes 8. Sensor nodes in large quantities are used 9. Have high redundancy 10. In remote and hard-to-reach areas, WSN is deployed | 1. There is only one type of medium used in Ad hoc networks: radio waves. 2. An application-independent network is used in Ad hoc. 3. It is heterogeneous in type. 4. Ad hoc networks are address-centric. 5. In Ad hoc networks, the traffic pattern is point-to-point. 6. They can support common services 7. Here, nodes can be any wireless device. 8. Compared to WSNs, fewer sensor nodes are used. 9. Have low redundancy 10. It can be deployed in any environment |
SIMILARITIES BETWEEN WSN AND AD HOC NETWORKS
Till now we have covered the difference between a wireless sensor network and an Ad hoc network, but there are also some similarities between the two networks.
In the case of wireless sensor networks vs. Ad hoc networks, the similarities are:
- Both are infrastructure-less wireless networks.
- Routing techniques are more or less the same.
- In both above-mentioned networks, the topology can change over a period of time.
- Nodes can be operated on a battery
- Both use unlicensed spectrum
MARKET DEMAND FOR WSN AND AD HOC NETWORKS
When we talk about WSN, there are three variables that push the development of WSN:
1. WIRELESS EFFECT
The demand for wireless connectivity is increasing every day, as it’s now a trend to go wireless. Thus, wireless technology has a very wide range and is used for sensing, monitoring, and control.
2. ECONOMIC DRIVING FORCES
Wireless sensor networks can reduce overall operational and labor costs and also bring good social benefits. Moreover, it will reduce the power consumption of devices and relieve traffic congestion.
3. TECHNOLOGY DRIVING FORCES
The advancement of technology will keep reducing the cost of hardware and software. In addition, the WSN market will also benefit from low-priced radio frequency modules.
This is the same case with Ad hoc networks; their market is also agitated by the above-given points. Similar to WSN, the ad hoc network is also infrastructure-less and features simple deployment.
The following situations are deemed suitable for ad hoc networks:
- If it is not possible to install the network equipment beforehand
- When it is necessary to quickly self-organize the network
- If the communication equipment is destroyed,
- And a distributed network is required.
SUMMING UP,
Both wireless sensor networks and Ad hoc networks are growing technologies that also hold great application potential. Therefore, integrating them with the infrastructure network will meet the demands of the object market and will also generate more new market opportunities.
Nevertheless, Hope this comparison of wireless sensor networks vs. Ad hoc networks helps
Do you need help with your IoT project? We specialize in wireless sensor networks (WSN) and would be happy to assist you. Connect with us today.
For more guidance and information, read our blog.
FAQ
The wireless sensor network is a group of sensors that can communicate wirelessly. These groups of sensors can communicate within their communication range and are capable of operating in changing environments.
One of the main advantages of Ad-hoc networks is that the nodes on ad-hoc networks don’t have to rely on any hardware or software. Thus, it can be connected and communicated effortlessly. Additionally, ad-hoc networks can be set up temporarily anywhere and at any time.
Ad hoc networks are mainly for data communication and have no sensing ability. They can be mobile (MANETs) or stationary, and there is no network centre.