IoT technology is becoming more and more mature daily and is offering intriguing solutions in all fields. IoT offers practical solutions that can be implemented in different industries.
In this article, we will talk about an important component of IoT- the IoT Gateway.
IoT devices need an IoT gateway that serves as a central hub for communication with external networks and to transmit and receive data from the cloud.
If you see, a lot happens at ground level in the IoT. Devices communicate with each other over a network; devices communicate with the cloud; and vice versa. Managing all these processes can be overwhelming sometimes. But the Internet of Things gateway can solve it.
Let’s find out how.
IOT GATEWAY: A BRIDGE BETWEEN IOT DEVICES AND SERVERS
We always say the Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of interconnected devices that collect and exchange data with each other and the cloud over the Internet.
Now, in the middle of this complex interconnected network stands the IoT gateway, to make the communication flow less complex.
An IoT gateway is a compact-sized physical device that transmits information from IoT devices to the cloud. Thus bridging the gap between IoT devices and servers.
Why do you need an IoT gateway?
In some IoT solutions, organizations deploy a bunch of IoT devices. However, it can be difficult to monitor and manage each of these devices individually. If the device has varied power and connectivity requirements, it gets more challenging.
However, an IoT gateway connects different types of IoT devices running on varied interfaces and protocols to the Internet.
So, we can say that an IoT gateway somewhat works like your network router. It is a link between IoT devices and the cloud. All the data from the IoT devices will pass through the IoT gateway and reach the cloud. This data transmission happens both ways. The Internet of Things gateway allows bidirectional data flow between the cloud and the IoT device. On top of this, the best IoT gateways can also handle device management tasks such as updating the firmware.
With technological advancement, these IoT gateway devices not only route the traffic but also preprocess the data locally at the edge and then send it to the cloud, making things simpler.
Hence, the IoT gateway also summarizes and aggregates the data received from numerous IoT devices to reduce the volume of the data and then forward it to the cloud.
So, the answer to why you need an IoT gateway is—that the IoT gateway improves the response time and minimizes network transmission costs.
Also Read: The difference between IoT platform and IoT gateway
HOW DOES AN IOT GATEWAY WORK?
Now that it’s quite clear, what is an IoT gateway? Let’s understand how an IoT gateway works with an example of a smart agriculture system.
A smart agriculture system comes with several sensors deployed in several fields. These sensors collect various soil-related information like temperature, moisture, NPK value, pH, CO2, and salinity.
Each sensor comes with a microcontroller that is responsible for data collection and transfer. The sensor and microcontroller, together, form a sensor node. (However, let’s call it “sensor” to avoid confusing things.)
The sensor node cannot operate with the data locally, so it passes the data to the cloud. All the sensors use low-power short-range communication protocols to send the data to the gateway.
Here, the gateway processes and aggregates the data and passes it further to the cloud through the internet. The pre-processing of the data locally is done to reduce network latency and is referred to as edge computing.
I know what you must be questioning right now.
Why can the sensor nodes not send the data directly to the cloud?
Well, this is not the optimal solution because every sensor should have enough power capacity and proper equipment for an Ethernet connection. Both of these are rare cases.
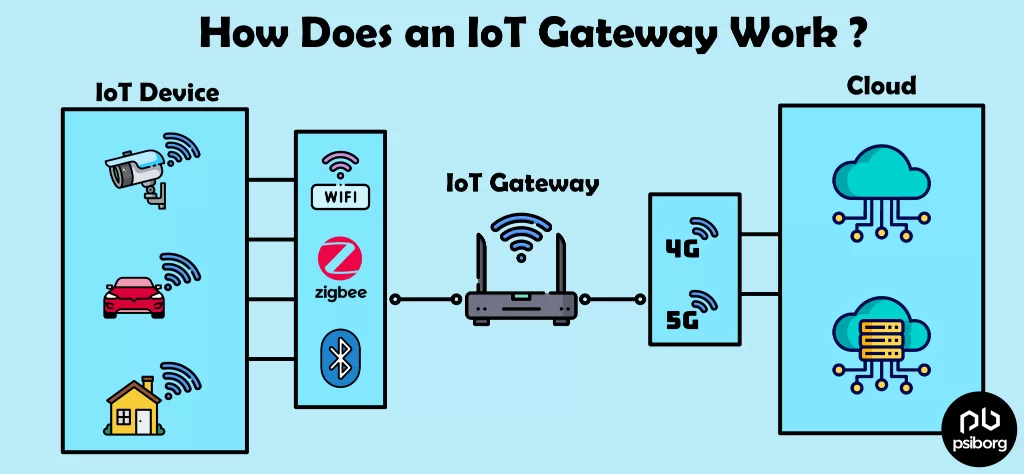
IOT GATEWAY ARCHITECTURE: IN BRIEF
The most common gateway architectural design includes the gateway itself, which is not equipped with any sensors. The gateway software embedded in the device collects the data from the sensors, preprocesses the data, and sends the result to the data center.
1. IOT GATEWAY DEVICE HARDWARE
An IoT gateway hardware contains a processor, IoT sensors, a protection circuit, and connectivity modules like ZigBee, Bluetooth, WiFi, and more. The type of hardware, its speed, and its memory space are based on the OS and the IoT gateway device.
Moreover, the end-user application is also greatly responsible for the design of the IoT hardware.
2. OS
The choice of operating system (OS) is also largely based on the IoT application.
For instance, if a gateway is created for a medium-scale application, then a Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) is used. However, if the gateway is designed for complex operations, then Linux is considered the best choice.
3. HARDWARE ABSTRACTION LAYER (HAL)
The hardware abstraction layer is for the portability of the IoT software. This layer in architecture is to make the software design independent of the hardware. Henceforth, the time and cost required to port the developed software application to a different hardware platform are reduced.
4. SENSOR STACK
As the name implies, this layer consists of software stacks that serve as interfaces with IoT sensor modules. A specific software stack is integrated based on the sensor interface that the IoT gateway supports. A few examples of integrated software stacks are– ZigBee, 6LoWPAN, BLE, and more.
5. DEVICE CONFIGURATION
This layer includes device management and device configuration. An IoT gateway device is required to keep track of all connected devices/sensors. In addition to this, all the sensor management and configuration are performed at the Internet of Things gateway itself.
Therefore, it becomes more important to configure the IoT gateway device for managing IoT sensor settings, properties, and access control.
6. FOTA
Firmware Over The Air (FOTA) updates ensure that the IoT gateway software is updated with recent versions of the security patches, OS, firewalls, and more.
So, within the IoT network, the gateway periodically checks for firmware updates in the cloud and triggers the update.
7. DATA COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL
For cloud communication, the IoT gateway should connect to the cloud over Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and 4G/5G modem. Here, the underlying communication layer is the UDP or TCP IP protocol.
Protocols like MQTT, CoAP, XMPP, and AMQP are used to maintain standardization.
8. DATA MANAGEMENT
The aforementioned incorporates data streaming, data filtering, and data storage. Here, the IoT gateway maintains the data from the sensor nodes to the gateway and also from the gateway to the cloud.
The task here is to minimize data transmission delays and ensure data fidelity.
9. CLOUD CONNECTIVITY MANAGER
This architectural layer is responsible for smooth connectivity with the cloud and also handles reconnections, device states, and gateway device authentications.
10. CUSTOM APPLICATIONS
The IoT gateway app is custom-designed according to the business’s needs. These gateway applications communicate with all the services and functions from the layers to manage data in an efficient, secure, and responsive manner.
11. GATEWAY DATA TRANSFER
The IoT gateway is connected to the internet for data transfer. However, the GPRS network is mostly preferred for connectivity. The data comes with in-built intelligence to determine which data should be transferred over the network for processing.
WHAT FUNCTIONS DOES AN IOT GATEWAY PERFORM?
Some of the most important IoT gateway functions are listed below:
COMMUNICATION WITH THE CLOUD
This is the main goal of an IoT gateway. It connects the sensor nodes to the cloud via 4G/5G or WiFi. It is a bidirectional communication where the data collected by the sensor goes to the cloud and a command from the cloud goes to the gateway.
This provides centralized control over the data flow. In addition, sensors that do not support internet connectivity can receive it via an IoT gateway.
ROUTE THE TRAFFIC
It’s pretty obvious: the gateway acts as a router and manages the traffic flow. The IoT gateway acts as a central traffic management system, making it easier to control and analyze the data.
SUPPORT MULTIPLE TRANSFER PROTOCOLS
You might be aware that sensors use different communication protocols, such as BLE, ZigBee, RFID, LoRaWAN, or LoRa.
Data is transferred through more power-intensive protocols, such as cellular wireless and Ethernet, by the gateway.
Consider it this way, each device speaks a different language, and the IoT gateway helps them communicate and send the right information to the cloud.
ISOLATION OF SENSOR NODES
By transmitting all the data to the cloud, the gateway shields the sensor node from public internet access. It also acts as a firewall for sensors by not allowing direct connections.
EDGE COMPUTING
This is the best part of using an IoT gateway- edge computing. Before passing data to the cloud, gateways can filter and summarize it locally. In this way, the overall data flow is reduced, IoT devices’ response time increases and the cost of data transmission is also reduced.
LOCAL STORAGE OF DATA
The gateway comes with local storage capacity to cache data when it’s not connected to the cloud. Thus, all the data remains safe.
SECURITY
The Internet of Things has a reputation for displaying a low level of security. Due to its advanced encryption and unauthorized access control, an IoT gateway is a good solution here.
BENEFITS OF INTERNET OF THINGS GATEWAY
With so many features, a gateway sure does have many advantages. Some of the advantages of using a gateway in an Internet of Things system are listed below:
- Protocol translation
- Data aggregation
- Edge computing
- Security
- Scalability
- Reliability
- Economical
IOT GATEWAYS, EDGE COMPUTING, AND SECURITY
IoT is all about untouched data insights and automation. There can be some IoT devices that produce large amounts of data. Getting huge amounts of data is beneficial, but it can also be a problem if there are many similar devices in an IoT ecosystem and all these devices individually send data to the cloud.
The IoT device sucks up the company’s available internet and incurs high costs for cloud storage.
That is why there is edge computing. With the use of edge computing, the total volume of data that has to be sent to the cloud will be reduced, thus reducing both the cost and internet consumption.
For example, if an IoT device is installed in a mall for footfall counting. It would make sense to send all the raw footage to the cloud every single minute for data processing.
However, rather than uploading all the footage in real-time, it’s more effective to process all the collected data at the edge. The edge device can differentiate between important and not-so-important data. For example, the footage of the gate when no one is entering the mall.
Thus, the edge device takes the data, reviews it, and sends it to the gateway device, which further transmits the data to the cloud.
Nevertheless, the IoT does come with some security risks. Thus, processing IoT data on edge devices will significantly reduce the amount of data sent to the cloud. This way, only limited data is transmitted to the cloud.
TO WRAP UP,
IoT gateways are important for managing IoT devices, and they also help an organization reduce security risks and IoT-related internet consumption.
IoT gateways can be used in probably all IoT systems, for example- in real-time soil health monitoring, forest fire detection, video surveillance systems, water quality monitoring, kiosk management, and much, much more.
Now that you understand the importance of including an IoT gateway in an IoT ecosystem, why not build an IoT system for your business?
PsiBorg Technologies is an IoT-service-providing company that specializes in offering custom IoT solutions to companies of all sizes.
If you plan to implement an IoT gateway or an entire IoT system in your business, give us a call.
FAQ
An IoT gateway is a compact-sized physical device that transmits information from IoT devices to the cloud. Thus, bridging the gap between IoT devices and servers. IoT gateway acts as a wireless access protocol and gives IoT devices access to the internet.
A gateway comes with local storage capacity to cache data when it’s not connected to the cloud. Thus, all the data remains safe. Processing the IoT data on edge devices will significantly reduce the amount of data sent to the cloud. This way, only limited data is transmitted to the cloud, and data security is achieved.
The only difference between an Internet of Things gateway and an IIoT gateway device is that the Industrial one is typically deployed on the plant floor, close to the manufacturing devices and sensors at the edge.