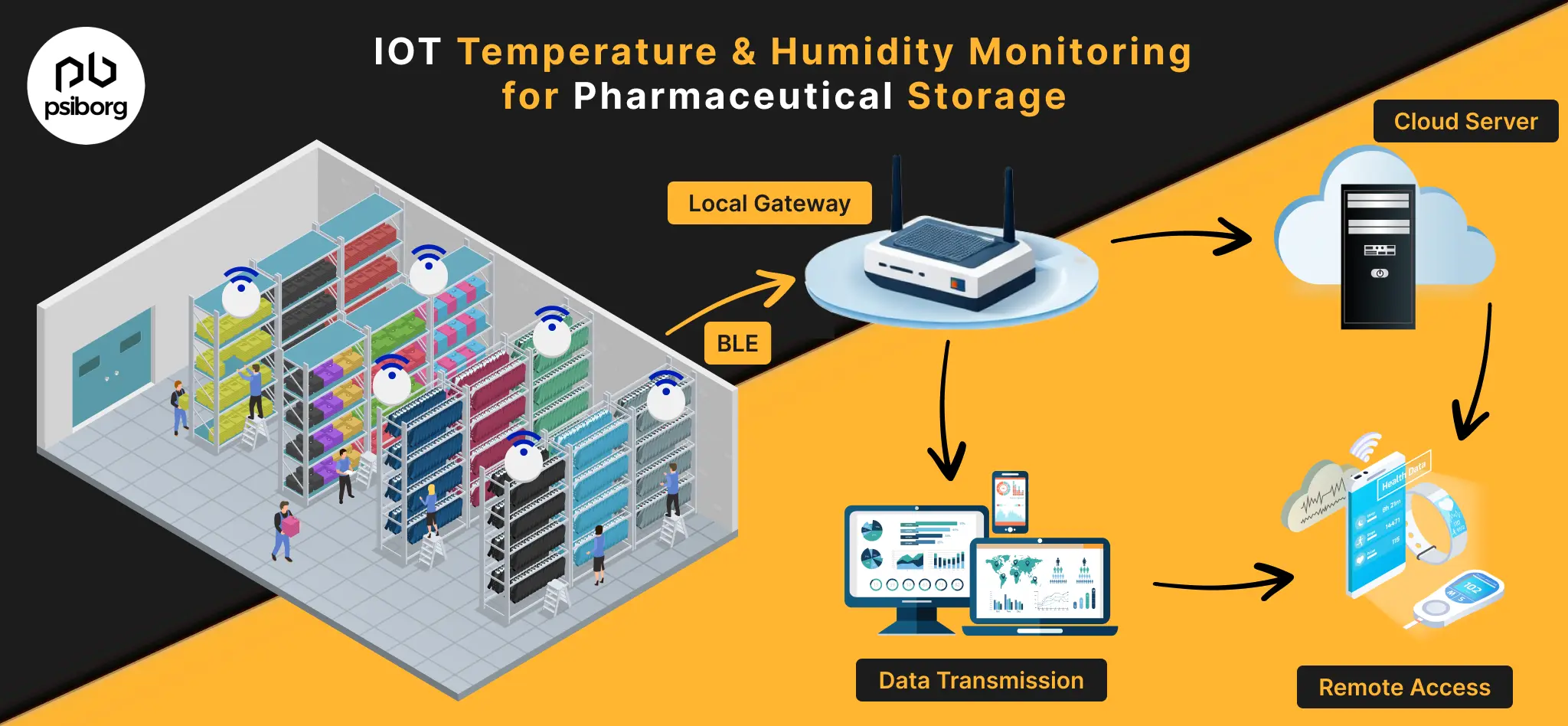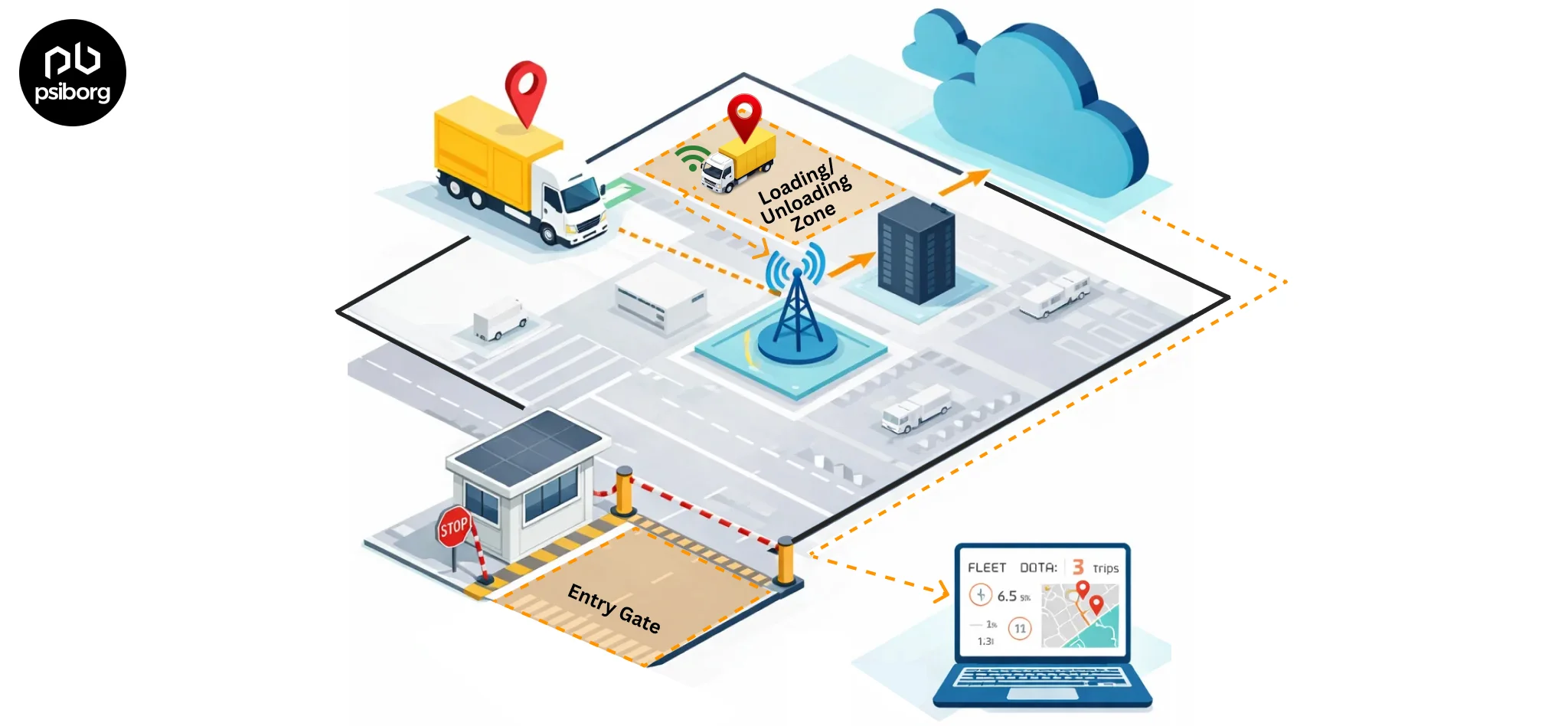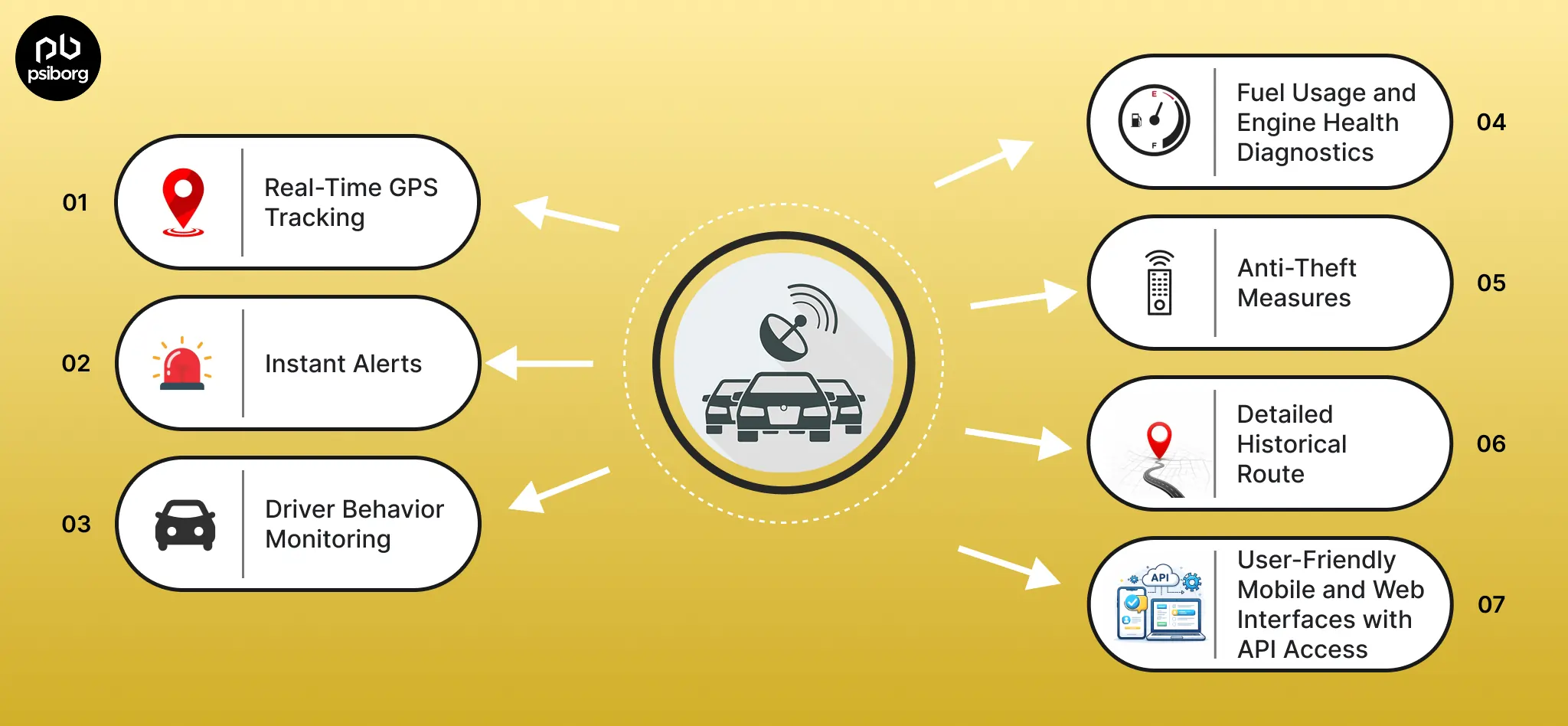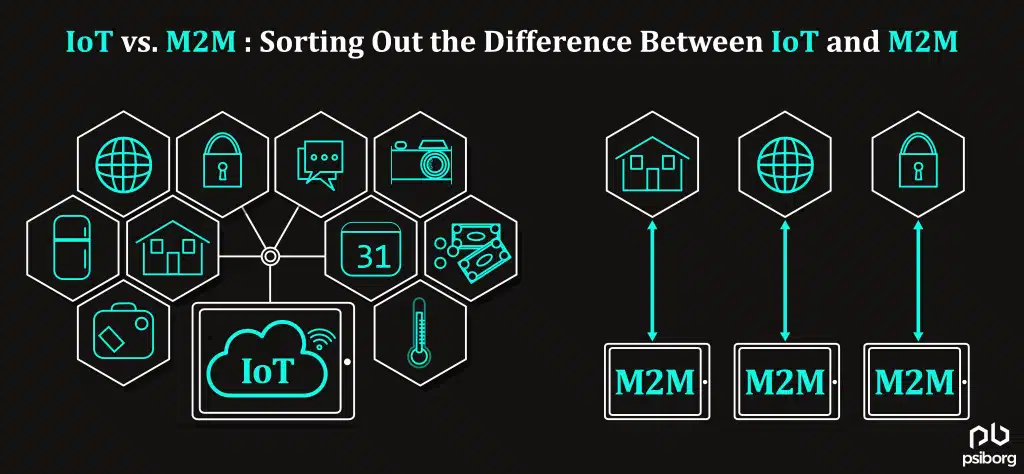
In this daily evolving world of technology, IoT is always the topic of discussion. Looking at the Google search queries, it is very clear that people are confused about the difference between IoT and M2M. Although it’s quite obvious to get confused between technologies when new technology gets introduced daily in the market.
The difference between Machine-to-Machine (M2M) and the Internet of Things (IoT) is very real. So, today’s post is an attempt to clear the air between IoT and M2M.
For all the readers skimming through a blog, here’s a quick comparison.
IoT stands for “Internet of Things.” This includes all networks that connect objects and devices that function with IP addresses. This also includes communication and transfer of data between connected devices.
Whereas M2M is Machine-to-Machine communication. It is needed for remote monitoring and access to machines for data exchange.
Both IoT and M2M are used for sharing data, but they are two different concepts that differ in the way they achieve connectivity.
Let’s dig deep to understand the difference between IoT and M2M.
EXPLAINING THE INTERNET OF THINGS (IOT)
IoT connects various devices. These devices encompass sensors and actuators that are proficient in storing and retrieving information.
IoT forms a large network of interconnected physical devices. These devices collect the data, exchange it as necessary, and create an entire ecosystem of connected devices.
IoT devices communicate with each other and the user to provide seamless automation in various domains.
IOT ARCHITECTURE
There are 4 stages of IoT architecture viz- sensing layer, the network layer, the data processing layer, and the application layer.
The sensing layer is the beginning of the IoT architecture and is liable for gathering data from different sources.
As the name suggests, sensing layers are comprised of sensors and actuators that are placed in the environment. These devices are linked to the network layer through wired/wireless communication protocols.
Whereas, the network layer is responsible for establishing communication and connectivity between the devices in the IoT system. It involves protocols and technologies like WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, 4G, and 5G that allow devices to connect and communicate with each other.
Furthermore, the data processing layer is the stage where the software and hardware components collect, analyze, and interpret data received from IoT devices. This layer basically reviews raw data and processes it to extract meaningful insights for better decision-making.
The application layer is the top layer, where the user is involved. The application layer provides user-friendly interfaces and functionalities and allows users to access and control IoT devices. This layer includes mobile apps, web portals, and dashboards.
IOT APPLICATIONS
Some of the most popular Internet of Things applications are:
- Smart home
- Wearables
- Smart cities
- IoT in Electric Vehicle Monitoring and Management
- Digital Health Devices
- Industrial automation………..and many more.
EXPLAINING MACHINE-TO-MACHINE (M2M)
M2M provides a point-to-point exchange of data between machines without an internet connection and doesn’t even require any manual human involvement. M2M was introduced in the market way before the establishment of the IoT. So, it’s worth pointing out that IoT needs M2M communication to be implemented; however, not all M2M applications have to do with IoT.
The communication process in M2M is done by either involving RFID, sensor monitoring, telematics, or remote monitoring.
Also, do you know that Nokia was among the first few companies to use M2M?
M2M ARCHITECTURE
The M2M architecture is divided into three main domains viz the M2M application domain, the M2M network domain, and the M2M device domain.
The M2M application domain offers applications that use M2M technology effortlessly. For example, the server and end-user applications.
The M2M network domain is a bridge between the M2M application domain and the device domain. It involves two parts- the M2M core and the M2M service capability.
Also, the M2M device domain contains all the devices that are connected to the M2M network easily.
M2M APPLICATIONS
The numerous applications for M2M are:
- Fleet management
- Remote monitoring
- ATM
- Vending machines
- Smart meters
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN IOT AND M2M
In M2M vs. IoT differences, various key factors come into play, such as how they both differ in terms of connectivity.
IoT depends on internet connectivity and cloud-based services, whereas M2M uses dedicated networks for direct machine-to-machine communication.
Let’s now take a closer look at the differences between IoT and M2M.
1. CONNECTIVITY: POINT-TO-POINT VS. NETWORK-BASED ACCESS
One of the prime differences between the IoT and M2M is the way communication is conducted.
M2M: Connectivity in M2M is achieved through point-to-point communication embedded by on-site hardware.
IoT: On the other hand, connectivity in IoT is network-based and achieved through IP networks. IoT communication between the two devices is established using a network protocol.
2. SOFTWARE DEPENDENCY
IoT vs. M2M also have distinctions on the basis of the extent to which they rely on software.
M2M: In the case of M2M, there is no such reliance. The technology is entirely hardware-based. Because devices communicate machine-to-machine, they don’t even need an internet connection.
IoT: However, in the Internet of Things, an active connection is required. IoT also relies on hardware, but it requires a platform for data processing and aggregation. So, it is said that IoT is both hardware and software-based.
3. SCALABILITY
M2M and IoT also show variations based on their scalability.
M2M: Machine-to-machine communication comes with a limited number of integration options. For effective communication, the devices need to be compatible. Also, it’s not possible for two machines with different tech stacks to connect using M2M.
This is the reason that M2M technology is used only for small-scale applications like maintenance.
IoT: However, IoT is designed for large-scale interaction. Plus, there are no hardware-based integration limits for IoT implementation.
4. DATA DELIVERY
IoT and M2M communication both facilitate data gathering. However, the way each of the two collects and delivers information is different.
M2M: In machine-to-machine, data is usually directed towards performing a one-shot task that improves the maintenance of objects. Moreover, M2M doesn’t have a common practice to transfer collected information and integrate it into a large-scale framework.
IoT: On the other hand, the IoT offers a wide range of possibilities in the area of data visualization and analysis. All the data collected by a sensor is integrated into an analytics system, where it can be compared with other collected data to gain insights. Therefore, the IoT is used by companies to improve work and team efficiency.
5. SUBJECTS OF COMMUNICATION
There is a clear distinction between the types of communication facilitated by M2M and IoT.
M2M: The machine-to-machine communication is solely device-based.
IoT: Whereas, the Internet of Things has a broader sphere of possible communication subjects. Apart from devices, it can also connect humans with machines, a device and a gateway, a gateway, and the data system, as well as two data systems.
There are some significant differences between IoT and M2M. However, these are not the only differences.
Below is a table for a quick rundown of the M2M vs. IoT difference.
| Points | IoT | M2M |
| Acronyms | Internet of Things | Machine-to-Machine |
| Intelligence | The IoT devices include set-ups that can make personal decisions without any outside interference. That’s why we call it ‘smart’ technology.” | M2M technology is intelligent only to a limited extent. |
| Connectivity | IoT devices communicate via a network and other wireless communications. | Point-to-point communication |
| Communication Protocols | TCP/IP protocols such as HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and Telnet | Traditional and less secure communication protocols are used. |
| Data Sharing | To improve the user experience, data is shared between applications. | Here, the data is shared between allowed connections. |
| Internet | IoT is nothing without the presence of the Internet. | M2M devices do not require an internet connection. |
| Examples | Smart wearables, smart cities, smart cars, smart homes, and more | Sensors and data information |
IOT VS. M2M: WHAT DOES YOUR BUSINESS NEED?
IoT and M2M both have different use cases, and they are both the best in their niches. So, there is no one-solution-fits-all approach.
So, what to choose between IoT and M2M depends on the purpose of your project.
For instance:
M2M technology is a better choice in case you:
- Need Point-to-point communication
- Wants to execute a minimum set of machine communications quickly and reliably.
- Need the project to be operational without a Wi-Fi connection
- Scalability isn’t your primary concern.
Moreover, IoT is considered a better option if your project:
- Requires real-time syncing of various devices.
- Needs scalability for several devices and users.
- Wants the data and devices to be compatible with multiple standards.
- Needs access to a fast and reliable WiFi connection.
TO SUM UP,
IoT and M2M are not synonymous technologies. Both IoT and M2M facilitate device-to-device communication, data collection, and storage but don’t require human supervision.
Moreover, they differ in terms of achieving connectivity and their scope.
So, this was it about IoT and M2M. I hope that after reading this blog post on the differences between IoT and M2M, you now have a clear understanding of each concept. If you’ve arrived at this page with the intention of developing a project that involves M2M or IoT, then you’ve certainly made the right choice.
Nevertheless, PsiBorg Technologies is an IoT solution provider, and our team of expert developers has experience in both M2M and IoT technologies.
At PsiBorg, we help you decide which technology – IoT or M2M – is best for your project.
To see the projects we have worked on, visit our success stories.
If you have any other doubts, don’t hesitate to contact us!
FAQ
IoT and M2M are the two technologies that you will hear about in every discussion of device networking. Both the technologies- IoT and M2M share similar objectives that is connecting smart devices without or with minimum human involvement for collecting and transmitting data.
Some of the common examples of M2M devices are smart home meters, asset tracking, automated supply chains, and telemetry services.
IoT creates an intelligent environment and provides a new way to interact with objects to capture real-time data from them. M2M, on the other hand, enables interaction between machines and is considered a special application of the IoT.