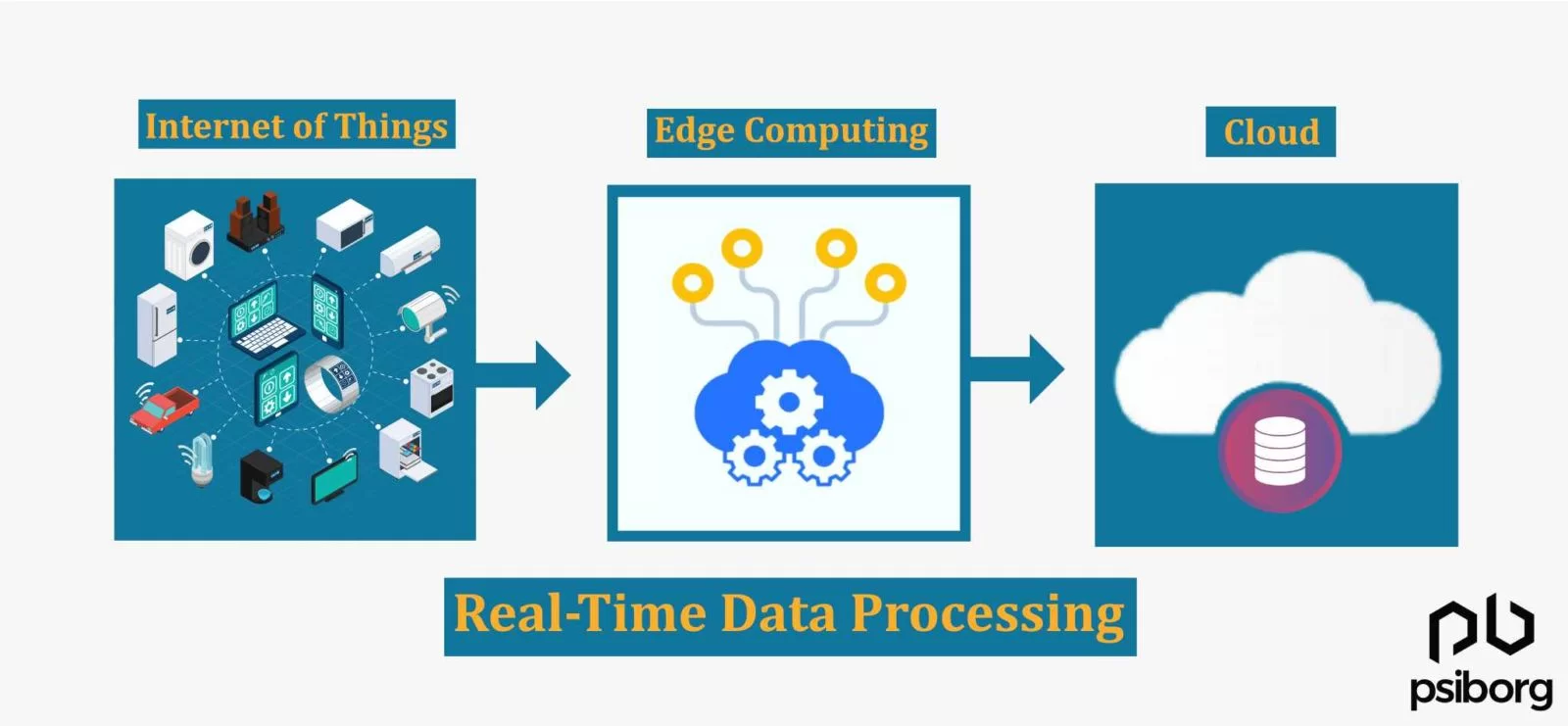
Edge computing is a distributed IT paradigm wherein client data is stored and processed as close to the originating source as possible. Whereas in cloud computing, data is processed at the central server. Edge computing and cloud computing in IoT play an equally important role.
In other words, edge computing brings data processing and storage resources away from the central data centre and closer to the data source itself. Let’s figure out when and where Edge computing and cloud computing in IoT are useful.
EDGE COMPUTING IN IOT: PROCESSING, ANALYTICS AND MORE
EDGE COMPUTING IMPROVES NETWORK LATENCY
Most IoT applications are basically high-end monitoring systems that collect and analyze data. After that take actions based on the insights obtained from the analysis of this data. It is sometimes done on an hourly or daily basis, or only when a specific event causes the trigger. Edge computing can prove to be useful for IoT when these insights are needed in real-time. By providing processing closer to the IoT device, data collection and analytics take place at a physically closer location (i.e. often within the same country or region, perhaps even on the premises, rather than in a large centralized data centre). Through this, network latency is minimized as the time for data to go back and forth between the data centre and back is shorter.
In this way, edge computing can prove to be beneficial for IoT applications that require real-time actions.
OPTIMIZATION OF BANDWIDTH REQUIREMENT
Most IoT-connected devices transmit very small packets of data back to a data management platform that processes this data to yield insights. This is fine with data being streamed to a platform running in a centralized cloud. But in the future, with a predicted explosive increase in the number of connected devices, this may strain operators’ existing networks. Even if individual data packets are only a few bytes, when this is being streamed in real-time from very many devices in a relatively small geographic area, For instance, in a manufacturing plant or a metro centre, the cumulative effect could be very large.
With edge computing, processing and filtering of IoT-generated data can be done closer to the devices, thereby optimizing bandwidth requirements.
EDGE COMPUTING PROVIDES BETTER SECURITY
One of the most glaring challenges in the IoT domain is security, especially as more and more devices are connected through IoT. Although edge computing is not more secure than a private cloud, it does have the benefit of being more local. When considering locations that have different data protection laws than where the data is being generated, edge computing can have good security advantages. Especially when the edge servers are located on the periphery of data sources, companies can control all access to the servers that store the information.
IOT EDGE PLATFORMS: IOT REQUIREMENTS FOR EDGE COMPUTING
The efficient functioning of Edge platforms for IoT applications requires certain IoT-specific requirements to be met.
For example, some IoT applications that require AI, ML or data analytics at the edge may have certain hardware requirements, such as servers with the necessary GPU capacity. Edge gateways for IoT devices will also have to support connectivity for a wide range of IoT device communications such as LoRaWAN, Sub-1 GHz, 6lowpan and Bluetooth, and also connectivity via cellulars such as NBIoT and LTE M and Wi-Fi technology.
Besides, operators have to keep in mind the type of IoT platform they are using and how compatible it is with their edge infrastructure. Many operators with IoT businesses rely on third-party vendor cloud platforms to manage their IoT networks. With the demand for edge applications growing, platform vendors are investing more resources in introducing capabilities to make their edge platforms better.
AWS IOT CLOUD
The aforementioned AWS IoT Core is a managed cloud service that lets connected devices easily and securely interact with cloud applications and other devices. It supports billions of devices and trillions of messages and can process and route those messages to AWS endpoints and to other devices reliably and securely. With AWS IoT Core, your applications can keep track of and communicate with all your devices, all the time, even when they aren’t connected.
GOOGLE IOT
It is a fully managed service to easily and securely connect, manage, and process data from globally dispersed devices.
Google IoT Core, along with other services on Google Cloud, provides a complete solution for collecting, processing, analyzing, and visualizing IoT data in real-time to support improved operational efficiency. IoT Core supports the standard MQTT and HTTP protocols. Thus, you can use your existing devices with minimal requirements for firmware updates.
Suggested Reading: THINGS EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW ABOUT EMBEDDED SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT.
WHAT IS CLOUD COMPUTING?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.
KEY ADVANTAGES OF IOT CLOUD COMPUTING
Multiple connectivity options
There are many connectivity options available in IoT cloud computing, thereby ensuring large network access. People make use of different types of devices to access cloud computing resources: mobile devices, tablets, laptops, etc.
Internet-based service
Since Cloud computing is a web-accessed service, there is complete ease and convenience for developers in IoT development.
Scalability advantages
One of the most valuable aspects of cloud computing is the scalability it offers. Users of cloud computing platforms can scale the service according to their needs. With speed and flexibility, you have the option of expanding storage space and altering software settings. This characteristic of cloud computing has enabled deep computing power and storage.
Better collaboration and coordination at work
With cloud Computing clients can benefit from pooling resources. It aids in collaborative projects and helps in building closer connections between users.
Higher security
As the numbers and scale of IoT-enabled devices and applications increase, and automation grows, cyber security concerns become quite apparent. With its robust and reliable authentication and encryption protocols, cloud solutions provide companies with the highest security and privacy.
Cost-effective
IoT cloud computing is cost-effective because you only pay for the resources you use.
A key IoT challenge is deploying software updates to edge devices without interrupting the already running services. Nevertheless, Kubernetes provides an ecosystem to IoT which can run microservices that progressively roll out changes achieving zero service downtime.
COMPARISON BETWEEN CLOUD COMPUTING AND EDGE COMPUTING
Let us understand the comparison between the two through the key features of these two technologies.
CLOUD COMPUTING
- It is highly centralized.
- Possesses high processing and computing power.
- Has high latency.
- Its processing capabilities are powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- It’s cyber secure
- It has a very high storage capacity
EDGE COMPUTING
- It is decentralized.
- Also has the lowest latency and is thus useful in applications where latency is a concern.
- Saves bandwidth as data processing and storage are done close to the data source.
- It has limitations in its processing and networking capabilities.
- There are data privacy and cybersecurity concerns.
An example of an IoT Edge cloud system that takes advantage of both Edge and cloud computing is healthcare facilities and other emergency systems that require immediacy in IoT service delivery.
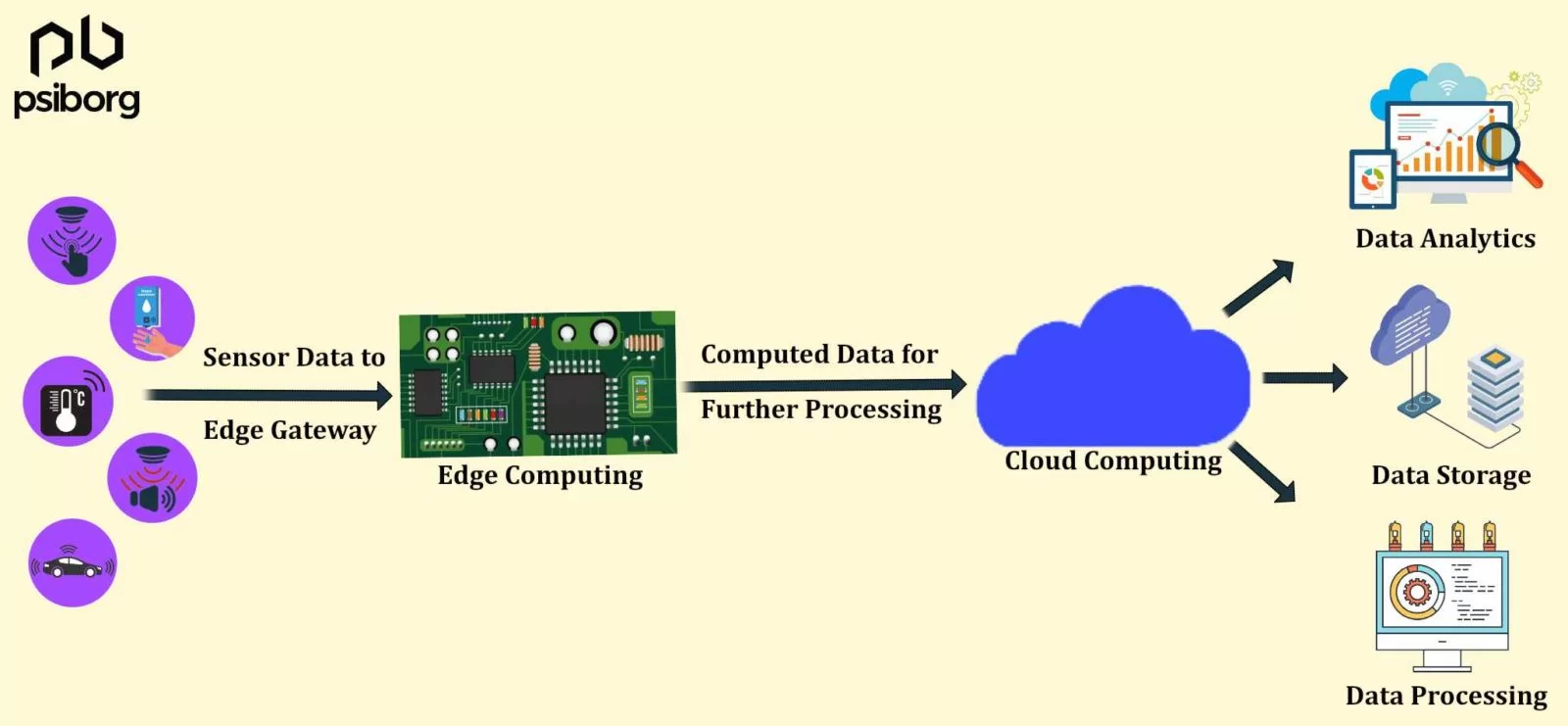
Edge Gateway devices sit at the intersection of cloud and IoT device nodes and sensor devices connecting over a network. Data collected from wireless sensor networks or other IoT devices will be transmitted through gateways(Data is computed at gateways) to the cloud(for further processing). The analyzed data received from IoT Devices is then stored in the cloud and from there it is provided as a service to the users.
In these situations, Edge computing helps in achieving decreased latency, whereas cloud computing helps achieve high data processing capabilities.
Also, Read- How do Sensor devices communicate data to the edge gateway? and COMPUTING AT THE CLOUD AND EDGE IN THE IOT.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it can be said that although edge and cloud computing have their own strengths and weaknesses. When the two combine, they can really bring greater efficiency to the IoT ecosystem.
PsiBorg is a full-stack IoT Development service provider, having immense experience in developing IoT solutions for global deployment.